AAVS1 Safe Harbor Gene Targeting
What are AAVS1 Safe Harbor Landing Pad Cell Lines?
A pre-engineered cell line with integrated genetic elements that facilitate simple payload exchange for your specific promoter and gene of interest. The landing pad construct is targeted to the AAVS1 safe harbor locus for stability and contains a florescent marker for downstream screening applications. Landing pad cell lines are offered as off the shelf products that have undergone rigorous testing and validation upfront. The product is available in a variety of cell backgrounds.
Design Features
- Interchangeable promoter and expression cassette
- Unique Cre/Lox sites flanking each module
- Single copy integration into the AAVS1 Safe Harbor locus
- mKATE2 expresses a red fluorescent protein – for identifying and sorting for successful integration
Benefits
- Rapid and robust Cre-mediated exchange with plasmid or PCR amplicon with your gene of interest (GOI) flanked by matching Lox sites
- Stable expression of the far-red fluorophore mKATE2
- EF1α promoter is active in a wide variety of cell types
- Select for mKATE2 negative population by FACS sorting
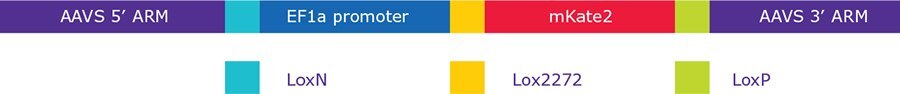
Figure 1.Illustration of landing pad construct inserted in AAVS1 safe harbor locus. The EF1α promoter and mKATE2 gene are flanked and separated by lox sequences for easy recombination by the Cre protein.
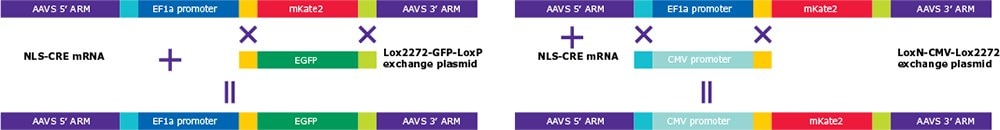
Figure 2.Exchange of Landing Pad payload exchange using Cre recombinase and targeting vector with appropriate LoxP elements.**
The landing pad construct features a promoter and mKATE2 payload flanked by homology arms. Each segment is separated by unique loxp sites that do not recombine with one another.

Figure 3.Overview of steps in the Landing Pad cell line engineering process.
Exchange of the promoter or payload requires a simple nucleofection with cre recombinase and a DNA donor containing complimentary loxp sites. Cells can then be screened for integration via loss of mKATE signal (FACS). This design makes engineered cell lines accessible to more researchers than ever before. Additionally, our Cell Design Studio™ Team can make use of landing pad cell lines in our custom engineering services.
Click here to watch our webinar to learn more on the generation of a landing pad T cell line useful for a T cell receptor customization.
Jurkat T Lymphocytes
Jurkat T lymphocytes are a human, acute T cell lymphoma cell line isolated in the late 1970s from the peripheral blood of a young male patient suffering from T cell leukemia. The cells possess a pseudodiploid karyotype and have been characterized as expressing CD3 and, upon stimulation, interleukin-2. This line has also been used to determine the cytotoxicity of the cytolethal distending toxin (CDT) holotoxin and its components and the study of expression of bisphenol A exposed estrogen receptor-β (ERβ) and estrogen-related-receptor-α (ERRα) in vitro.
Benefits
- Single copy integration into the AAVS1 Safe Harbor locus; confirmed by junction PCR (jPCR) and CNV analyses.
- Continuous stable expression of the far-red fluorophore mKATE2.
- Rapid and robust Cre mediated exchange with matching lox2272 and loxP plasmid or PCR amplicon with your gene of interest (GOI).
- Select for mKATE2 negative population by FACS sorting.
- Have an enriched mKATE2 negative population within 2-4 weeks.
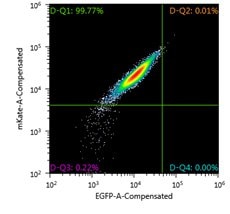
FACS analysis of Jurkat Landing Pad clone prior to Cre-mediated exchange
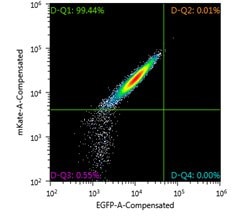
FACS analysis of Jurkat Landing Pad clone Cre-only nucleofection control, one week post-nucleofection
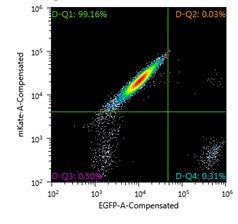
FACS analysis of Jurkat Landing Pad clone nucleofected with Cre mRNA and targeting DNA vector containing EGFP for exchange, one week post-nucleofection
A549 Cancer Cells
A549 is a human lung carcinoma cell line isolated in 1972 from a lung tumor of a male patient suffering from carcinoma. The cells possess a hypotriploid karyotype, express EGFR and mutant KRAS. A549 cells have been used to study proliferation induced by IGF1 as well as growth inhibition by BChTT. In addition, these cells have been used to model alveolar type II pneumocyte differentiation.
Benefits
- One copy of the cassette integrated into the AAVS1 Safe Harbor locus; confirmed by junction PCR (jPCR) and CNV analyses.
- Continuous expression of the far-red fluorophore, mKATE2.
- Rapid and robust Cre mediated exchange with matching lox2272 and loxP plasmid or PCR amplicon containing your gene of interest (GOI).
- Select for mKATE2 negative population by FACS sorting or other fluorescence assisted instrument.
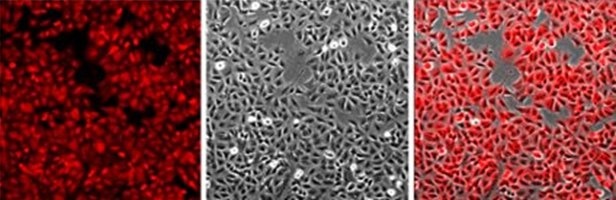
A549 10X Imaging of A549 cells landing pad cell line. Left, image demonstrates the homogenous expression of mKATE2 in the cell line. Middle, a brightfield image of the same culture showing 90% confluent A549 culture. Right, merged image showing all the cells in the culture are stably expressing mKATE2.
A375 Cancer Cells
A375 cancer cells are a human malignant melanoma cell line isolated from a 54 year old female. The cells possess a hypotriploid karyotype. The cell line produces rapidly growing amelanotic melanomas in anti-thymocyte serum treated NIH Swiss mice. A375 cells have been used to obtain paracrine factors for prolonged culture of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). It has also been used to study oncolytic activity of the peptide LTX-315.
Benefits
- One copy of the cassette integrated into the AAVS1 Safe Harbor locus; confirmed by junction PCR (jPCR) and CNV analyses.
- Continuous expression of the far-red fluorophore, mKATE2.
- Rapid and robust Cre mediated exchange with matching lox2272 and loxP plasmid or PCR amplicon containing your gene of interest (GOI).
- Select for mKATE2 negative population by FACS sorting or other fluorescence assisted instrument.
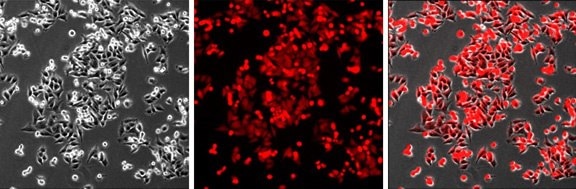
A375 10X Imaging of A375 cells landing pad cell line. Left, image demonstrates the homogenous expression of mKATE2 in the cell line. Middle, a brightfield image of the same culture showing 90% confluent A375 culture. Right, merged image showing all the cells in the culture are stably expressing mKATE2.
HCT-116 Cancer Cells
HCT-116 cancer cells are a human colorectal carcinoma cell line isolated from the colon of an adult male. The cells possess a near diploid karyotype and express carcinoembryonic antigen. Cells are tumorigenic in nude mice and form colonies on agarose. HCT-116 cells have been used to study the importance of cyclin D1 for the activity of lithocholic acid hydroxyamide (LCAHA) In addition the cells have been used in studies pertaining to iron uptake.
Benefits
- One copy of the cassette integrated into the AAVS1 Safe Harbor locus; confirmed by junction PCR (jPCR) and CNV analyses.
- Continuous expression of the far-red fluorophore, mKATE2.
- Rapid and robust Cre mediated exchange with matching lox2272 and loxP plasmid or PCR amplicon containing your gene of interest (GOI).
- Select for mKATE2 negative population by FACS sorting or other fluorescence assisted instrument.
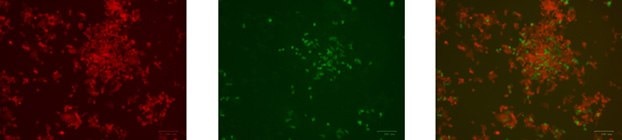
HCT-116 cells 72 h post nucleofection with GFP control exchange plasmid and cre mRNA. The Left image demonstrates the mKate2 expression of the non-exchanged cells. The middle image shows the cells in which GFP cDNA has been exchanged into the AAVS1 landing pad locus. The image on the right shows the overlay of the GFP with the mKATE showing that the cells have switched and can be isolated using FACS sorting or by other single cell cloning methodologies.
THP-1 Cells*
Derived from the peripheral blood of a 1 year old male with acute monocytic leukemia. THP-1 cells have Fc and C3b receptors and lack surface and cytoplasmic immunoglobulins. These cells also stain positive for α-napthhyl butyrate esterase, produce lysozymes and are phagocytic (both latex beads and sensitized erythrocytes). THP-1 cells can also restore the response of purified T lymphocytes to Concanavlin A, show increased CO2 production on phagocytosis and can be differentiated into macrophage-like cells using for example DMSO.
Benefits
- THP-1 cells are highly sensitive to exogenous DNA making gene editing challenging.
- Cre mediated DNA exchange allows for more efficient integration of genes of interest using mKATE negative selection.
- Expands capabilities of THP-1 cells for genetic engineering.
* Availability
- Custom engineering of THP-1 through the gene editing experts in Cell Design Studio
- Cell Design Studio performs the Cre/Lox recombination for any number of derivative lines desired
- Deliverables include assay-ready, derivative THP-1 cell lines
**Targeting vectors are not provided.
FAQs
What if I don’t see a cell line I am interested in? Will the landing pad be put into other cell lines?
Currently, we offer only these 4 lines as off-the-shelf products. However, if you are interested in having landing pad technology in a cell line not listed here, our Cell Design Studio team will be happy to work with you to design that custom cell line. Please contact us.
Is the AAVS1 gene important? Does integration here affect cell growth or phenotype?
The majority of reports show that AAVS1 is not essential and that disruption of this gene does not affect cell growth or phenotype. The AAVS1 gene has low expression and has been well-documented in the literature as a safe harbor site.
What is the rate of exchange?
The rate of exchange, or rate of integration, varies with the cell line. For some cell lines, an enrichment step may be required before single cell cloning.
Can I put in my gene of interest under its own promoter, not EF1alpha?
Absolutely! The advantage of this line is the modular control. There are 3 unique Cre/Lox sites in the cassette: one before the promoter, one between the promoter and the fluorescent reporter, and one after the fluorescent reporter. To exchange both the gene and promoter, you would design your exchange plasmid to include the first and third Cre/Lox sites. To exchange only the gene, your exchange plasmid would contain the second and third Cre/Lox sites.
Will this result in significant overexpression? How many copies of my gene will be present?
Unlike viral transduction, the expression of your gene of interest can be controlled by changing the promoter (i.e. integrate a weak promoter for lower expression or strong promoter for high expression). You could also integrate an inducible promoter for even more controlled expression. The landing pad is only present on one allele of AAVS1 so the copy number of your integrated gene will be one, unlike the varied copy number associated with viral integration.
Does a pool show enough purity to be used for downstream testing?
Yes. Since the landing pad cassettes are used for targeted integration in a single allele, you can sort the nucleofected cells and enrich a pool for loss of fluorescence. This is an advantage over viral integration which is random and varies in copy number.
Can I make other genetic manipulations in these lines, not through the landing pad site?
Yes! These cell lines are designed to be used as tools to enable complicated engineering. Under the purchase agreement, further gene editing including CRISPR KO/KI can be performed.
Can the Cell Engineering team help me design my experimental workflow?
Absolutely. Our expert Cell Engineering team can provide technical support for your workflow. Please contact us.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?