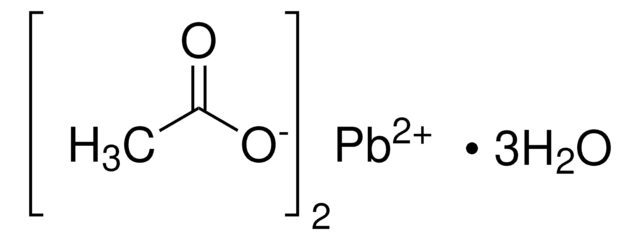
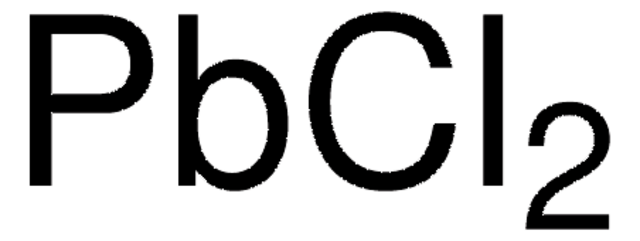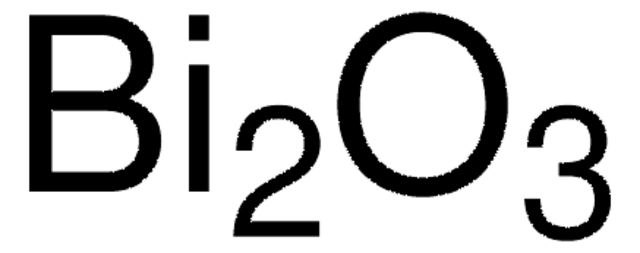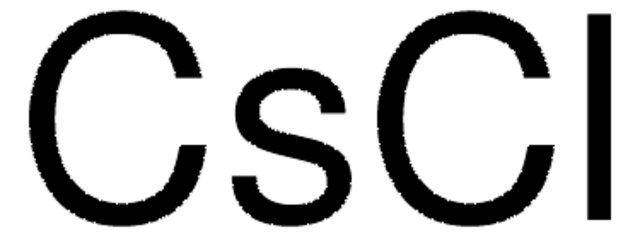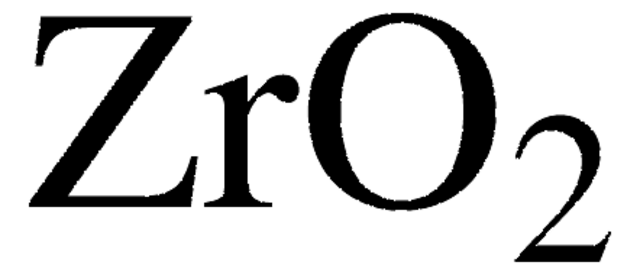449865
Lead(II) chloride
AnhydroBeads™, −10 mesh, 99.999%
Synonym(s):
Cotunnite
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
1 mmHg ( 547 °C)
Quality Level
product line
AnhydroBeads™
assay
99.999%
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: lead
impurities
≤15.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
particle size
−10 mesh
bp
950 °C (lit.)
mp
501 °C (lit.)
density
5.85 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Cl[PbH2]Cl
InChI
1S/2ClH.Pb/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
InChI key
HWSZZLVAJGOAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Legal Information
accessory
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 2 - Repr. 1A - STOT RE 1
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Since the first report of the low-cost dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) in 1991 by Gratzel and his coworker,1 dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) has been regarded as one of the most promising photovoltaic technologies because of their transparent and colorful characteristics, as well as low cost.
Colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) are semiconducting crystals of only a few nanometers (ca. 2–12 nm) coated with ligand/surfactant molecules to help prevent agglomeration.
The past several decades have seen major advancements in the synthesis of metal nanomaterials. Most recently, controlled synthesis has become versatile enough to regulate the exact number of atoms and ligands of very small metal nanoparticles, referred to as “clusters”.
Next generation solar cells have the potential to achieve conversion efficiencies beyond the Shockley-Queisser (S-Q) limit while also significantly lowering production costs.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service