All Photos(1)
About This Item
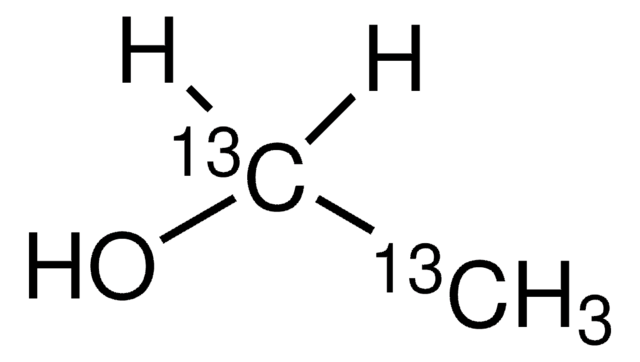
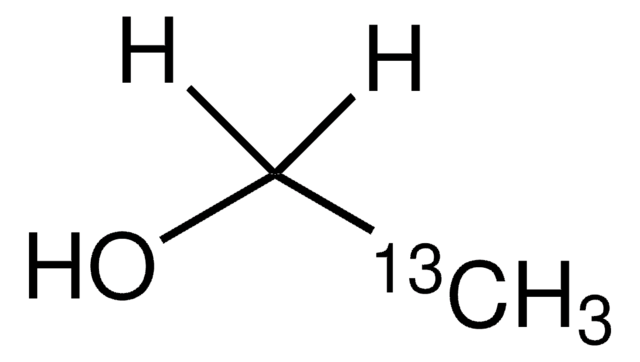
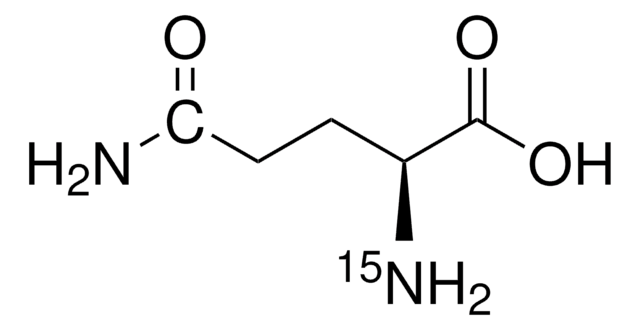
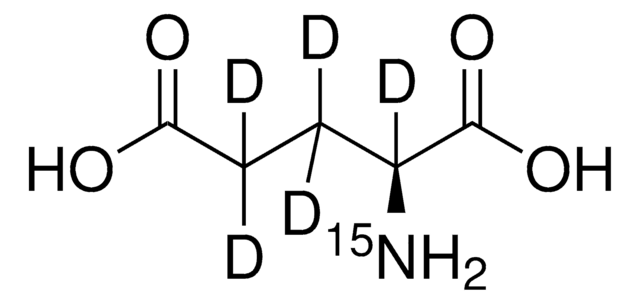
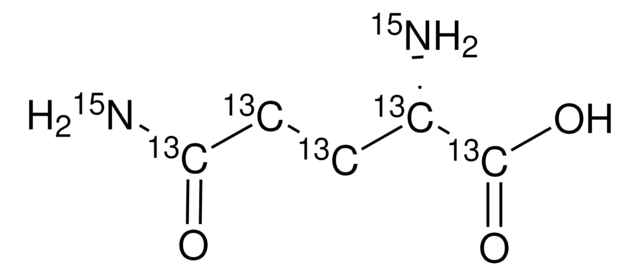
Linear Formula:
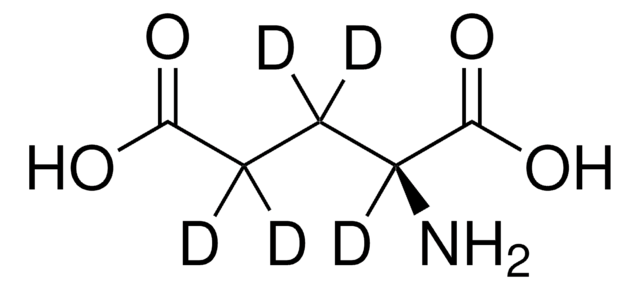
H2NCO(CD2)2CD(NH2)CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
151.18
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
Recommended Products
isotopic purity
98 atom % D
Quality Level
assay
98% (CP)
form
solid
optical activity
[α]25/D +33.0°, c = 2 in 5 M HCl
mp
185 °C (dec.) (lit.)
mass shift
M+5
SMILES string
[2H]C([2H])(C(N)=O)C([2H])([2H])[C@]([2H])(N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C5H10N2O3/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8/h3H,1-2,6H2,(H2,7,8)(H,9,10)/t3-/m0/s1/i1D2,2D2,3D
InChI key
ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-NKXUJHECSA-N
Related Categories
Packaging
This product may be available from bulk stock and can be packaged on demand. For information on pricing, availability and packaging, please contact Stable Isotopes Customer Service.
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Carolina Salazar et al.
Metabolites, 2(3), 398-428 (2012-01-01)
In spite of the large arsenal of methodologies developed for amino acid assessment in complex matrices, their implementation in metabolomics studies involving wide-ranging mutant screening is hampered by their lack of high-throughput, sensitivity, reproducibility, and/or wide dynamic range. In response
Alberto Valdés et al.
Scientific reports, 11(1), 5058-5058 (2021-03-05)
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease. Although hyperglycaemia has been determined as the most important risk factor, hypoxia also plays a relevant role in the development of this disease. In this work, a comprehensive metabolomic
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service