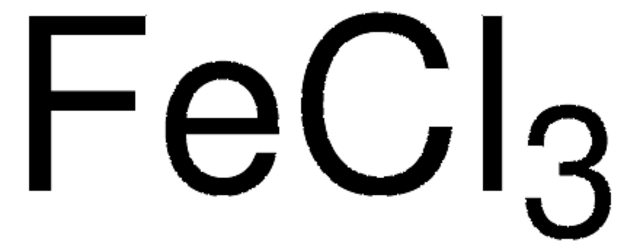701122
Iron(III) chloride
sublimed grade, ≥99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Ferric chloride, Iron trichloride, Molysite
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
sublimed grade
Quality Level
vapor density
5.61 (vs air)
vapor pressure
1 mmHg ( 194 °C)
assay
≥99.9% trace metals basis
form
powder or crystals
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: iron
greener alternative product characteristics
Catalysis
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
≤1000.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
mp
304 °C (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
greener alternative category
SMILES string
Cl[Fe](Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/3ClH.Fe/h3*1H;/q;;;+3/p-3
InChI key
RBTARNINKXHZNM-UHFFFAOYSA-K
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- polymerizations
- oxidations
- oxidative couplings
- reductions
- C-C bond formation
- Ferrier rearrangement
- multicomponent condensations
- Friedel-Crafts reactions
- cyclization′s
- glycosidation
- Prins-type cyclization
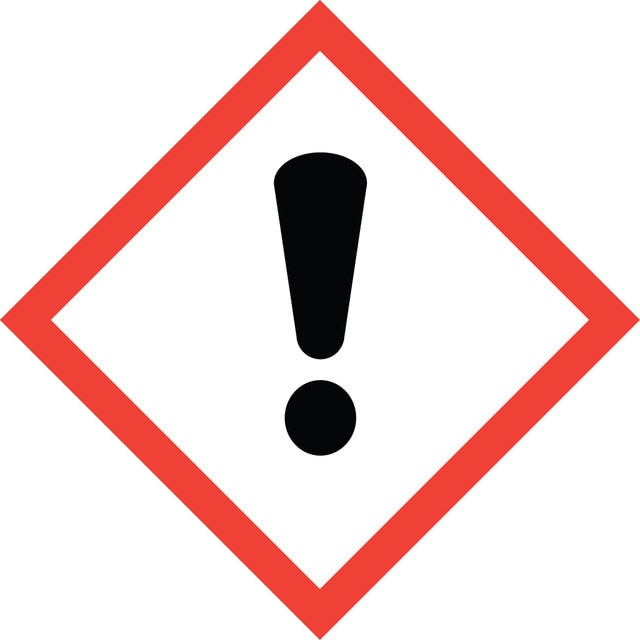
signalword
Danger
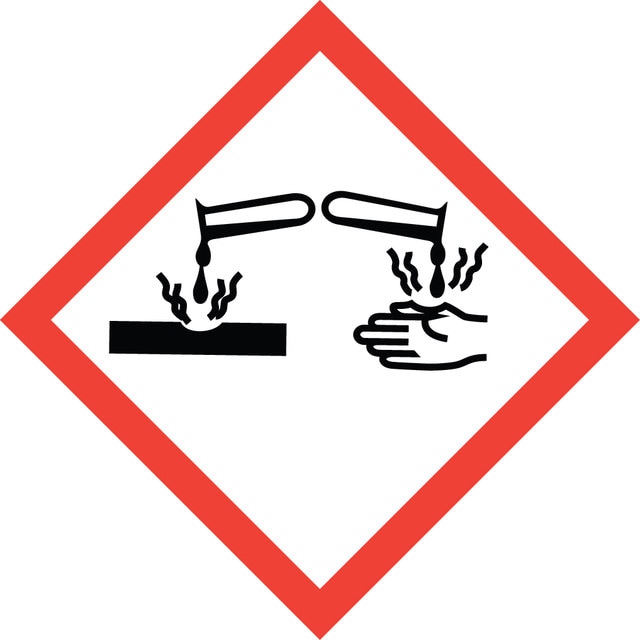
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class
8B - Non-combustible, corrosive hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Professor Randal Lee (University of Houston, USA) discusses design considerations for iron oxide magnetic nanospheres and nanocubes used for biosensing, including synthetic procedures, size, and shape. The effects of these variables are discussed for various volumetric-based and surface-based detection schemes.
Lithium-ion batteries represent a group of electrochemical devices used for electricity storage and have attracted a lot of attention in the past two decades due to their portability, rechargeability and low cost.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service