798088
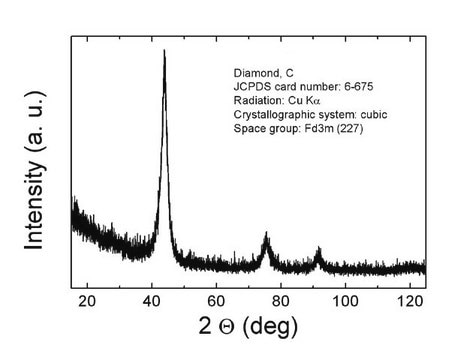
Fluorescent nanodiamond
Nitrogen vacancy ~3 ppm NV centers, 120 nm avg. part. size, 1 mg/mL in deionized water
Synonym(s):
Diamond nanopowder, Nanodiamonds
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
suspension
Quality Level
composition
Nitrogen vacancy, ~3 ppm NV centers
concentration
1 mg/mL in deionized water
avg. part. size
120 nm
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Properties & characteristics of Fluorescent Nanodiamonds & biofunctionalization strategies explained. Conjugation protocols for streptavidin functionalization, biotinylation & coupling biotinylated/streptavidin provided. FNDs may be used for labeling of low-level expressed targets, Bioimaging & Bioconjugation.
Fluorescent Nanodiamond Particles (FNDs)- Find properties and applications of nanodiamond particles.
Biomaterials science involves the design and fabrication of smart materials for studying, directing, or mimicking biology. For successful integration of biomaterials in biological research, a meaningful understanding of biological systems is required.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service