All Photos(1)
About This Item
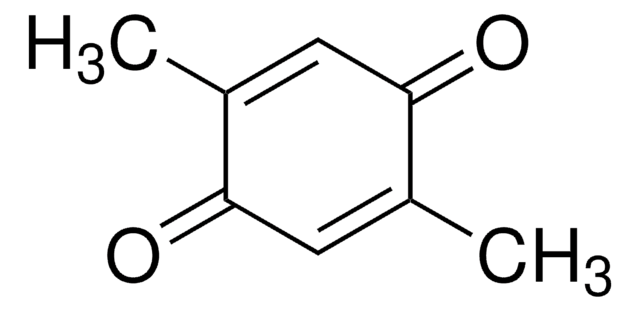
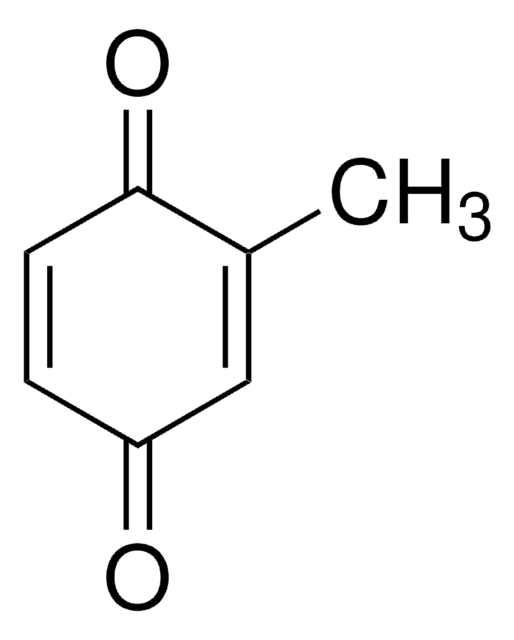
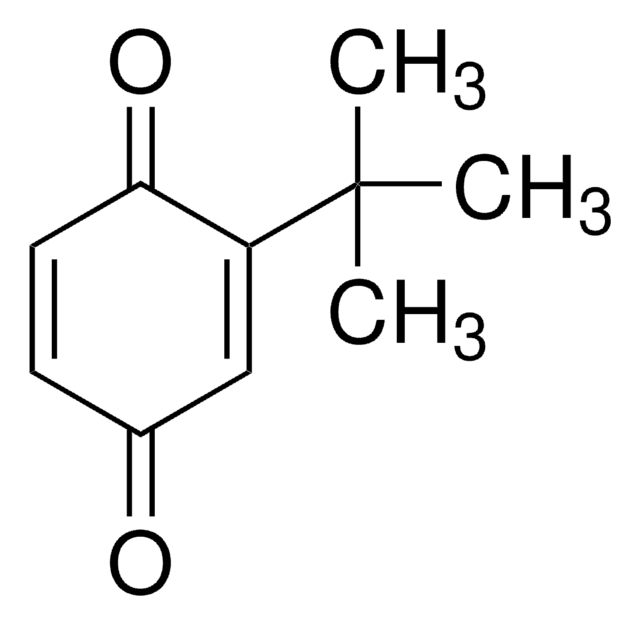
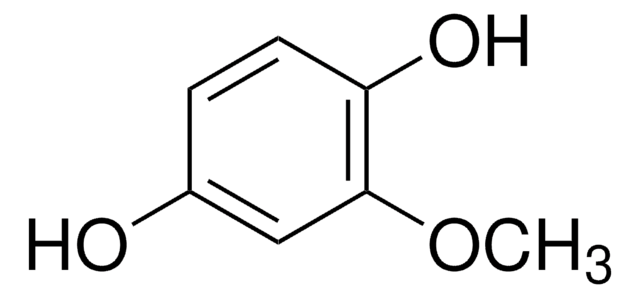
Linear Formula:
(CH3)2C6H2-1,4-(=O)2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
136.15
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
99%
form
solid
mp
71-73 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC1=CC(=O)C=C(C)C1=O
InChI
1S/C8H8O2/c1-5-3-7(9)4-6(2)8(5)10/h3-4H,1-2H3
InChI key
SENUUPBBLQWHMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
D Kim et al.
Chemistry & biology, 5(2), 103-117 (1998-03-13)
The temporal and spatial control of the transition from vegetative to parasitic growth is critical to any parasite, but is essential to the sessile parasitic plants. It has been proposed that this transition in Striga spp. is controlled simply by
Sam Hay et al.
The journal of physical chemistry. B, 111(13), 3488-3495 (2007-03-29)
The electrochemistry of 2,6-dimethylbenzoquinone (DMBQ) has been characterized for three different systems: DMBQ freely solvated in aqueous buffer; DMBQ bound to a neutral, blocked cysteine (N-acetyl-L-cysteine methyl ester) and the resulting DMBQ-bCys compound solvated in aqueous buffer; and DMBQ bound
A C Stewart
The Biochemical journal, 204(3), 705-712 (1982-06-15)
1. Photosynthetic electron transport from water to lipophilic Photosystem II acceptors was stimulated 3--5-fold by high concentrations (greater than or equal to 1 M) of salts containing anions such as citrate, succinate and phosphate that are high in the Hofmeister
Mustafa Odabaşoğlu et al.
Acta crystallographica. Section C, Crystal structure communications, 61(Pt 4), o240-o242 (2005-04-05)
Molecules of the title compound, C8H9NO2, are linked into sheets by a combination of C-H...N, O-H...N and O-H...O hydrogen bonds and C-H...pi interactions. The hydrogen bonds are arranged as described by the graph-set ring notations R(2)(2)(7) and R(3)(3)(5), and a
Argyrides Argyrou et al.
Biochemistry, 42(7), 2218-2228 (2003-02-20)
Lipoamide dehydrogenase catalyzes the reversible NAD(+)-dependent oxidation of the dihydrolipoyl cofactors that are covalently attached to the acyltransferase components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase, alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and glycine reductase multienzyme complexes. It contains two redox centers: a tightly, but noncovalently, bound
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service