D62403
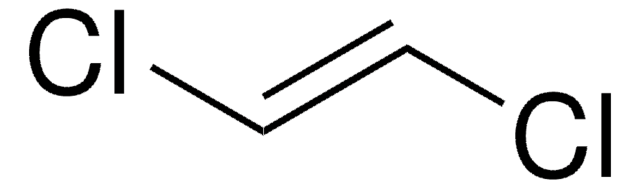
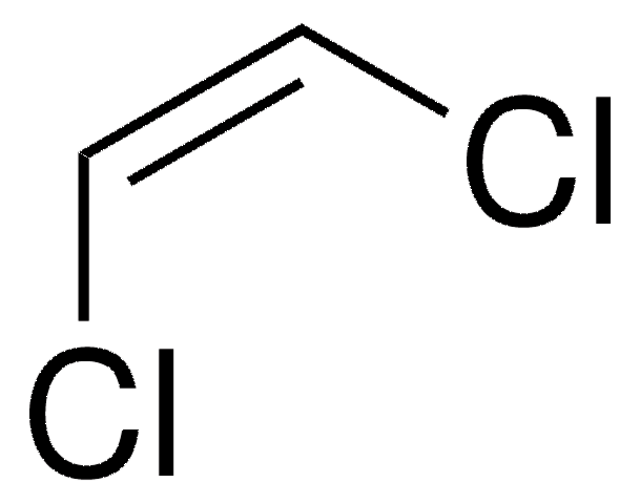
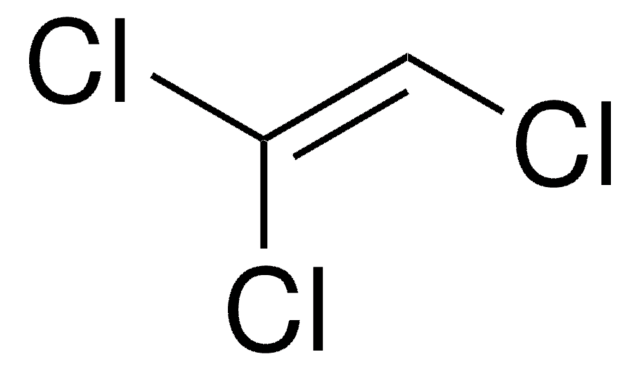
1,2-Dichloroethylene, mixture of cis and trans
98%
Synonym(s):
1,2-Dichloroethene, Acetylene dichloride, sym-Dichloroethylene
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
5.32 psi ( 20 °C)
Quality Level
assay
98%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.447 (lit.)
bp
48-60 °C (lit.)
mp
−57 °C (lit.)
density
1.265 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
Cl\C=C\Cl
InChI
1S/C2H2Cl2/c3-1-2-4/h1-2H/b2-1+
InChI key
KFUSEUYYWQURPO-OWOJBTEDSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Chloro-enynes from terminal alkynes via Sonogashira coupling.
- Trichloroethyl alkyl ketones by reacting with acyl chlorides via Friedel-Crafts reaction in the presence of aluminum chloride.
- (Ethenediyl)bis[thiazole] via Pd-catalyzed Stille-coupling reaction with 2-(tributylstannyl)thiazole.
accessory
signalword
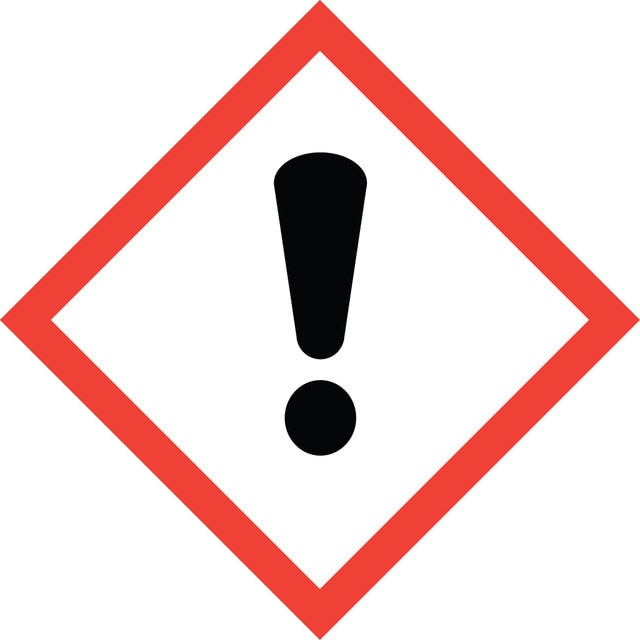
Danger
hcodes
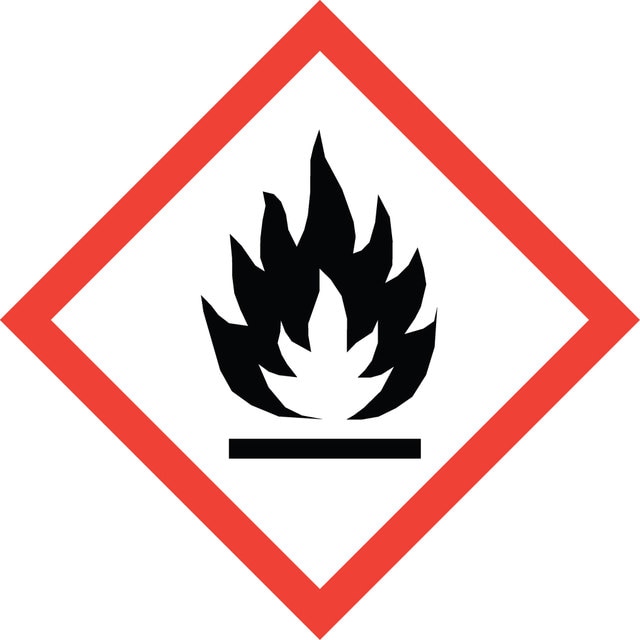
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Flam. Liq. 2
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
closed cup
flash_point_c
closed cup
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service