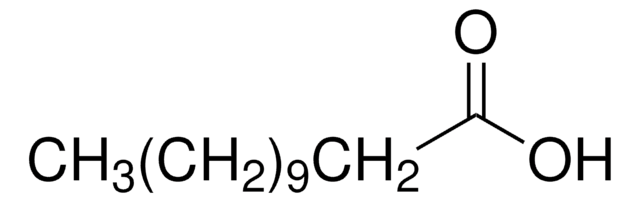W244910
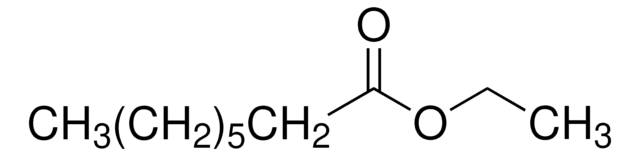
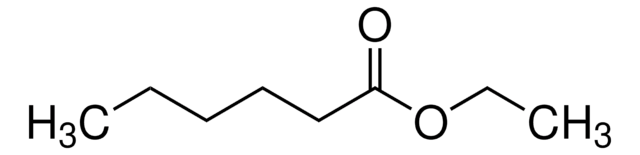
Ethyl octanoate
natural, ≥98%, FCC, FG
Synonym(s):
Ethyl caprylate
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
FG
Halal
Kosher
natural
Quality Level
agency
meets purity specifications of JECFA
reg. compliance
EU Regulation 1334/2008 & 178/2002
FCC
FDA 21 CFR 117
vapor pressure
0.02 mmHg ( 25 °C)
assay
≥98%
refractive index
n20/D 1.417 (lit.)
bp
206-208 °C (lit.)
mp
−48-−47 °C (lit.)
solubility
ethanol: soluble 1ml/4ml, clear, colorless (70% ethanol)
density
0.867 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
application(s)
flavors and fragrances
documentation
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
food allergen
no known allergens
organoleptic
banana; fruity; floral; pineapple
SMILES string
CCCCCCCC(=O)OCC
InChI
1S/C10H20O2/c1-3-5-6-7-8-9-10(11)12-4-2/h3-9H2,1-2H3
InChI key
YYZUSRORWSJGET-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
hcodes
pcodes
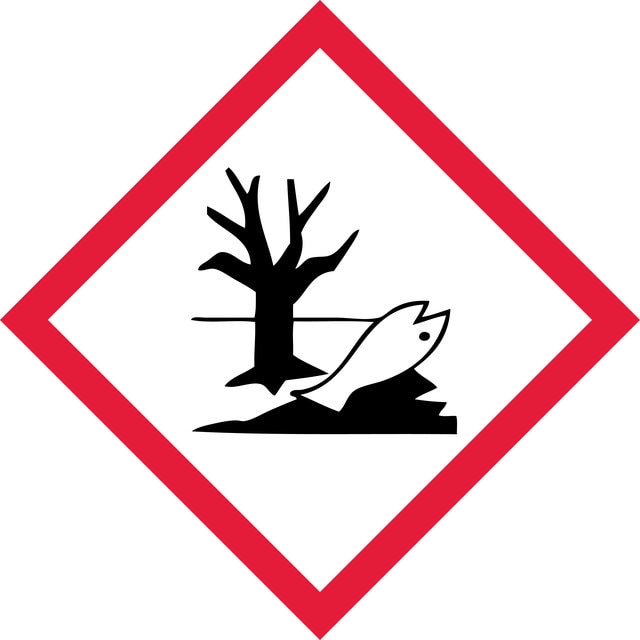
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
167.0 °F
flash_point_c
75 °C
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service