07-1232
Anti-Notch 1 Antibody, NT
serum, from rabbit
Synonym(s):
Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 precursor, Notch (Drosophila) homolog 1 (translocation-associated), Notch 1, Notch homolog 1, translocation-associated (Drosophila), Translocation-associated notch protein TAN-1, Neurogenic locus notch homolog pro
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
serum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
species reactivity
human, mouse
species reactivity (predicted by homology)
rat (immunogen homology)
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... NOTCH1(4851)
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
A previous lot of this antibody was diluted to 1:20,000-1:60,000 and used in a standard sandwich ELISA assay against the peptide immunogen.
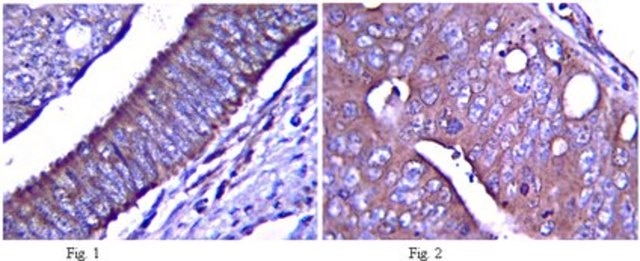
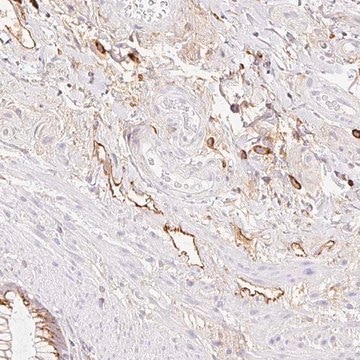
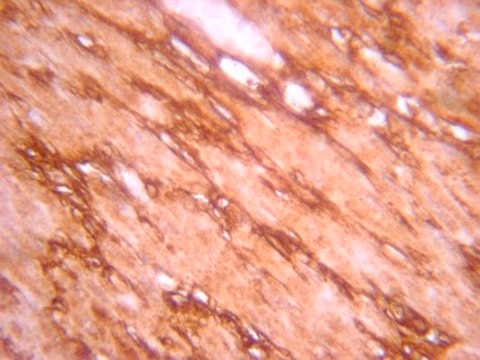
Immunohistochemistry(paraffin):
Representative testing from a previous lot.
Optimal Staining of Notch-1 With Citrate pH 6.0 Epitope Retrieval: Uterine Cancer
ELISA: A previous lot of this antibody was diluted to 1:20,000-1:60,000 and used in a standard sandwich ELISA assay against the peptide immunogen.
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Transcription Factors
Quality
Western Blot Analysis: 1:500 dilution of this lot detected cleaved NOTCH1 on 10 μg of Jurkat lysates.
Target description
Linkage
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Handling Recommendations: Upon first thaw, and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Analysis Note
Jurkate Cell Lysates. In fetal tissues, use spleen, brain stem and lung. In adult tissues use mainly lymphoid tissues.
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
recommended
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service