444250
MMP Inhibitor I
The MMP Inhibitor I controls the biological activity of MMP. This small molecule/inhibitor is primarily used for Protease Inhibitors applications.
Synonym(s):
MMP Inhibitor I, FN-439
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
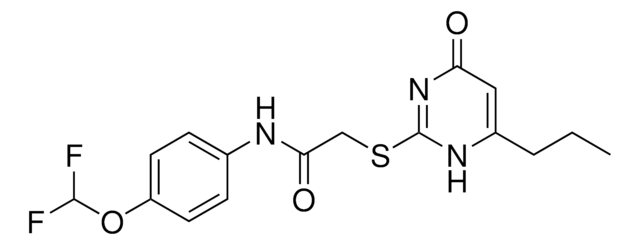
C23H34N6O6
Molecular Weight:
490.55
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
solid
potency
1 μM IC50
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
color
white
solubility
water: 1 mg/mL
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
A tetrapeptidyl hydroxamic acid that inhibits MMP-1 and MMP-8 (IC50 = 1.0 µM), MMP-9 (IC50 = 30 µM) and MMP-3 (IC50 = 150 µM). Retains its activity even after prolonged incubation with PRONASE Protease (Cat. Nos. 53702 or 537088) or human granulocyte elastase.
A tetrapeptidyl hydroxamic acid that inhibits interstitial and granulocyte collagenases (MMP-1 and MMP-8; IC50 = 1 µM), granulocyte gelatinase (MMP-9; IC50 = 30 µM), adn skin fibroblast stromelysin (MMP-3; IC50 = 150 µM). Retains its activity even after prolonged incubation with PRONASE Protease (Cat. No. 53702) or human neutrophil elastase.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cell permeable: no
Primary Target
MMP-1, MMP-8
MMP-1, MMP-8
Product does not compete with ATP.
Reversible: no
Warning
Toxicity: Standard Handling (A)
Sequence
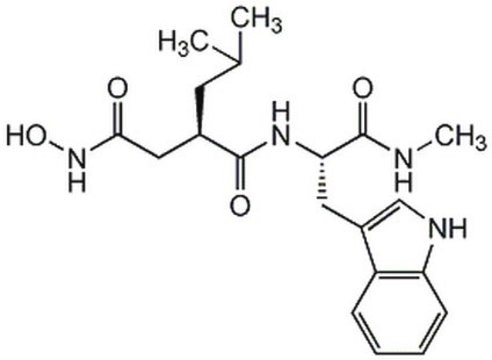
4-Abz-Gly-Pro-D-Leu-D-Ala-NH-OH [Abz = aminobenzoyl]
Reconstitution
Following reconstitution aliquot and freeze (-20°C). Stock solutions are stable for up to 1 month at -20°C.
Other Notes
Hagemamn, T., et al. 2004. Carcinogenesis25, 1543.
Odake, S., et al. 1994. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199, 1442.
Odake, S., et al. 1994. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199, 1442.
Legal Information
CALBIOCHEM is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Jörg Weiske et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 289, 175-192 (2004-10-27)
In epidermal cells desmosomes represent major sites of basolateral cell-cell contacts that play an important role for epidermal homeostasis. Excess or damaged cells are often removed by apoptosis. To release apoptotic cells from the tissue, intercellular contacts have to be
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service