8.00894
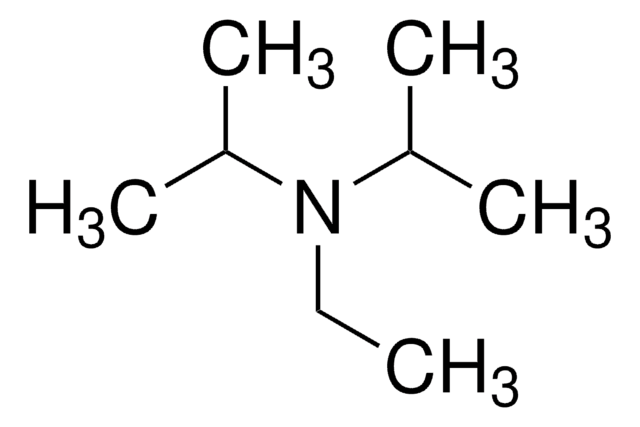
N-Ethyldiisopropylamine
for synthesis
Synonym(s):
N-Ethyldiisopropylamine, N,N-Diisopropylethylamine
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
14 hPa ( 20 °C)
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (GC)
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
240 °C
potency
200-500 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
expl. lim.
0.7-6.3 % (v/v)
pH
12.3 (20 °C in H2O, as an emulsion)
kinematic viscosity
0.88 cSt(20 °C)
bp
127 °C/1013 hPa
transition temp
flash point 9.5 °C
density
0.76 g/cm3 at 20 °C
storage temp.
2-30°C
InChI
1S/C8H19N/c1-6-9(7(2)3)8(4)5/h7-8H,6H2,1-5H3
InChI key
JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Application
- Dual Stimuli-Responsive Hybrid Polymeric Nanoparticles Self-Assembled from POSS-Based: Describes the synthesis of hybrid polymeric nanoparticles using N-Ethyldiisopropylamine in the assembly process (Yang et al., 2022).
- Magnetical Control of the Charge-Separated State Lifetime Realized by Covalent Attachment of a Platinum Complex: Details the use of N-Ethyldiisopropylamine in the preparation of magnetically controllable platinum complexes (Kozaki et al., 2021).
- Hybrid block copolymers of polyesters/polycarbonates and polypeptides synthesized via one-pot sequential ring-opening polymerization: Explains the initiation of polymerization with N-Ethyldiisopropylamine for creating hybrid block copolymers (Gradišar et al., 2018).
Analysis Note
Density (d 20 °C/ 4 °C): 0.755 - 0.758
Water (K. F.): ≤ 0.20 %
Identity (IR): passes test
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
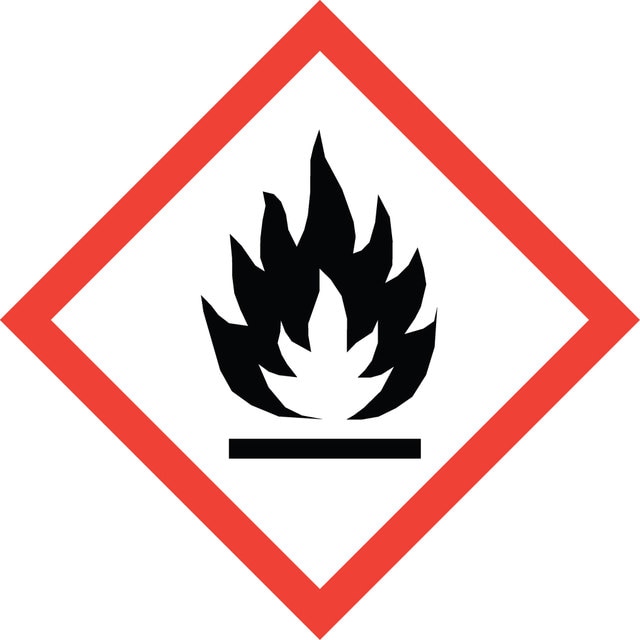
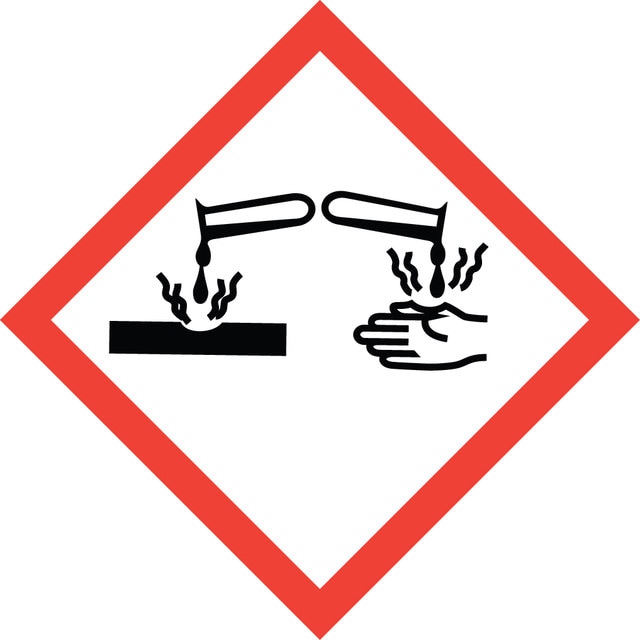
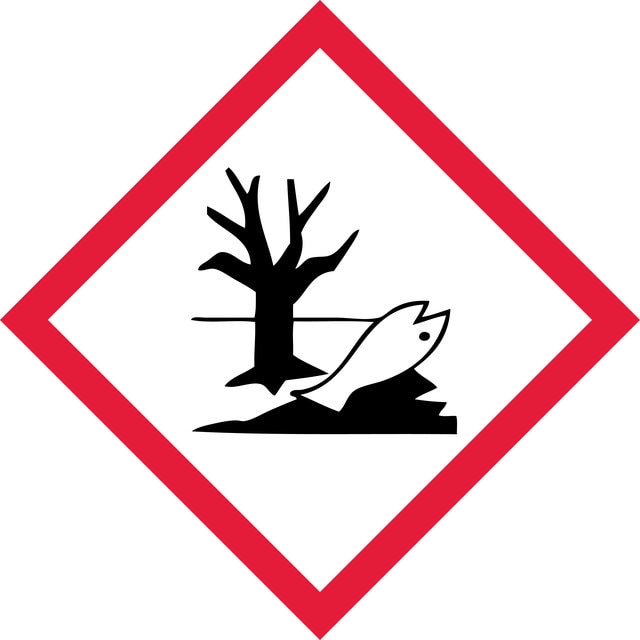
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
49.1 °F
flash_point_c
9.5 °C
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Related Content
Fmoc resin cleavage and deprotection follows the difficult task of detaching the peptide from the resin support and removing all the side-chain protecting groups of the amino acid residues to yield the desired peptide.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service