ABN991
Anti-phospho GLUT-1 Antibody (Ser226)
from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography
Synonym(s):
Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1, Glucose transporter type 1, erythrocyte/brain, GLUT-1, HepG2 glucose transporter, Human T-cell leukemia virus I and II receptor, Receptor for HTLV-1 and HTLV-2, phospho GLUT-1 (Ser226)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
purified by
affinity chromatography
species reactivity
mouse, human
species reactivity (predicted by homology)
horse (based on 100% sequence homology), canine (based on 100% sequence homology), bovine (based on 100% sequence homology), Xenopus (based on 100% sequence homology), rat (based on 100% sequence homology), rabbit (based on 100% sequence homology)
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
inhibition assay: suitable (peptide)
western blot: suitable
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
target post-translational modification
phosphorylation (pSer226 )
Gene Information
human ... SLC2A1(6513)
General description
Immunogen
Application
Western Blotting Analysis: An 1:200 dilution (5 µg/mL) from a representative lot detected TPA-induced phosphorylation of wild-type GLUT-1, but not GLUT-1 with S226A mution in lysates from Rat2 fibroblasts expsssing the respective constructs via retrovirus-mediated transfection (Courtesy of Dr. Richard C. Wang, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX).
Western Blotting Analysis: An 1:200 dilution (5 µg/mL) from a representative lot detected a time-dependent GLUT-1 Ser226 phosphorylation induction in serum-starved human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) upon VEGF treatment (Courtesy of Dr. Richard C. Wang, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected PKC activation-induced GLUT-1 Ser226 phosphorylation in human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) upon TPA (Cat. No. 500582 & 524400) treatment only the in the absence, but not in the presence, of PKC inhibitor Go 6983 (Cat. No. 365251) (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected a time-dependent GLUT-1 Ser226 phosphorylation induction in serum-starved human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) upon VEGF or angiotensin II treatment (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected comparable Ser226 phosphorylation induction of exogenously expressed wild-type GLUT-1 or K526E mutant in transfected Rat2 fibroblasts upon PKC activator TPA (Cat. No. 500582 & 524400) treatment (Cat. No. 365251) (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected PKC activator TPA-induced GLUT-1 Ser226 phosphorylation in serum-starved HeLa, human primary cardiac endothelial cells, EA.hy926 human endothelial cells, and bEnd.3 mouse brain endothelial cells (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected PKC-catalyzed Ser226 phosphorylation of GST fusion protein containing wild-type GLUT-1 Loop 6 (4th cytoplasmic domain) seuqnce, but not GST-Loop 6 fusions with R223P, R223Q, R223W, or S226A mutation, in in vitro kinase assays (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected a time-dependent GLUT-1 Ser226 phosphorylation induction in serum-starved human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) upon VEGF treatment (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
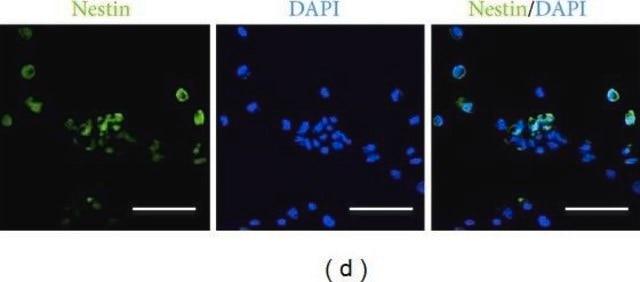
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected PKC activation-induced GLUT-1 Ser226 phosphorylation in the membrane ruffles of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) upon TPA (Cat. No. 500582 & 524400) treatment (Lee, E.E., et al. (2015). Mol. Cell. 58(5):845-853).
Note: Process lysate samples by warming at 50°C for 10 minutes prior to gel loading. Avoid heating samples at a temperature higher than 60°C, which can cause aggregation of the target protein.
Quality
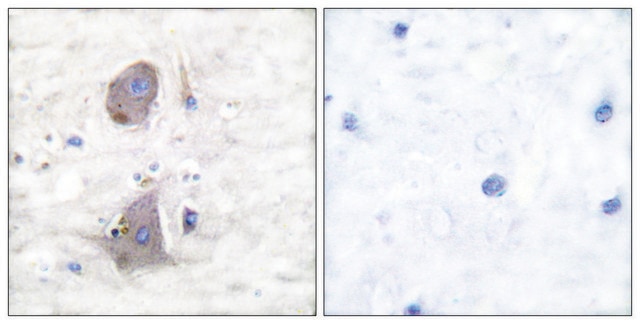
Western Blotting Analysis: 2.0 µg/mL of this antibody detected Ser226 phosphorylated GLUT-1 in lysates from PMA-treated HeLa cells.
Target description
Other Notes
Still not finding the right product?
Give our Product Selector Tool a try.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service