General description
Ubiquitin (Ub), a highly conserved 76-amino acid (8.6 kDa) protein that escorts proteins for rapid degradation to the multi-component enzymatic complex known as the 26S proteasome. Ubiquitin is initially produced as polyubiquitin-B or polyubiquitin-C precursor protein and its posttranslational cleavage yield multiple copies of identical 76-amino acid ubiquitin. Ubiquitin is involved in one of the most common post-translational modifications of cellular proteins, where it is linked covalently via its carboxyl terminus (Gly76) to lysine residues in target proteins. A given target lysine residue can be linked to one single ubiquitin molecule (monoubiquitylated) or to a chain of ubiquitins (polyubiquitylated). In a polyubiquitin chain, ubiquitin molecules can be linked through one of the seven lysine residues (K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, and K63) or through the ubiquitin N-terminus methionine 1 residue (which generates linear chains). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lysine 6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lysine 11-linked is involved in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation, lysine 29-linked is involved in lysosomal degradation, and Lysine 48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome. Affimer molecules are small proteins (~ 12 kDa) that bind to target molecules with similar specificity and affinity to that of antibodies. These engineered non-antibody binding proteins are designed to mimic the molecular recognition characteristics of monoclonal antibodies in different applications. It has been shown that each affimer molecule ca bind one ubiquitin molecule and the Affimer dimerizes to bind the two ubiquitin moieties of a diubiquitin in a linkage-specific manner. The K6 Affimer is reported to tightly bind to K6 diubiquitin in a highly specific manner. It can be used to detect K6 chains and with polyubiquitin enrichment it can detect even the endogenous levels of K6 chains. (Ref.: Michel, MA., et al. (2017). Mol. Cell. 68(1); 233-246).
Specificity
Anti-diUbiquitin K6 GFP/His-tag Affimer reagent detects K6 linked poly-ubiquitin chains with a KD of approximately 20 pM. Binding to other di-ubiquitin linkages is negligible.
Immunogen
Ubiquitin Lys6 specific Affimer reagent, Anti-Ubiquitin Lys6 specific Affimer reagent, Ubiquitin Lys6 specific Affimer Reagent GFP/His tag
Application
Quality Control Testing
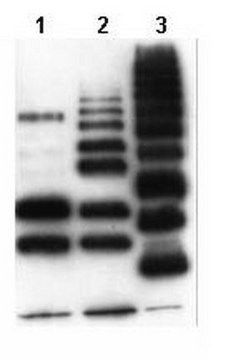
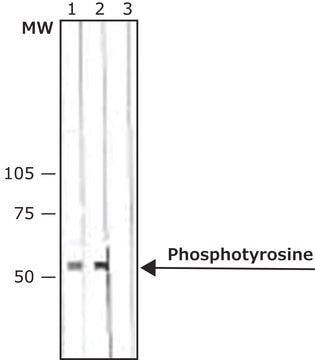
Evaluated by Western Blotting with Various K-linked di-ubiquitin chains.
Western Blotting Analysis (WB): A 1:1,000 dilution of this Affimer reagent detected di-ubiquitin K6-linkages.
Tested Applications
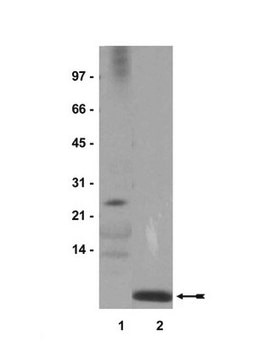
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot of this Affimer detected di-Ubiquitin Lys6. in Western Blotting applications (Michel, M.A., et. al. (2017). Mol Cell. 68(1):233-246).
Note: Actual optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user as specimens, and experimental conditions may vary with the end user
Anti-Ubiquitin Lys6 specific GFP/His-tag Affimer reagent, Cat. No. MABS1918, detects diubiquitin K6-linkage and is tested for use in Western Blotting.
Physical form
Purified GFP/His-tag Affimer reagent in buffer containing 100 mM Sodium Phosphate, 150 mM Sodium Chloride, 0.02% Sodium Azide, pH 7.4.
Storage and Stability
Recommend storage at +2°C to +8°C. For long term storage antibodies can be kept at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaws.
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.