11170376001
Roche
Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine
from mouse IgG1 (clone: BMC9318)
Synonym(s):
anti-BrdU, antibody
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
BMC9318, monoclonal
assay
90% (HPLC and SDS-PAGE)
form
solution
packaging
pkg of 50 μg (500 μl)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
isotype
IgG1
storage temp.
−20°C
Related Categories
General description
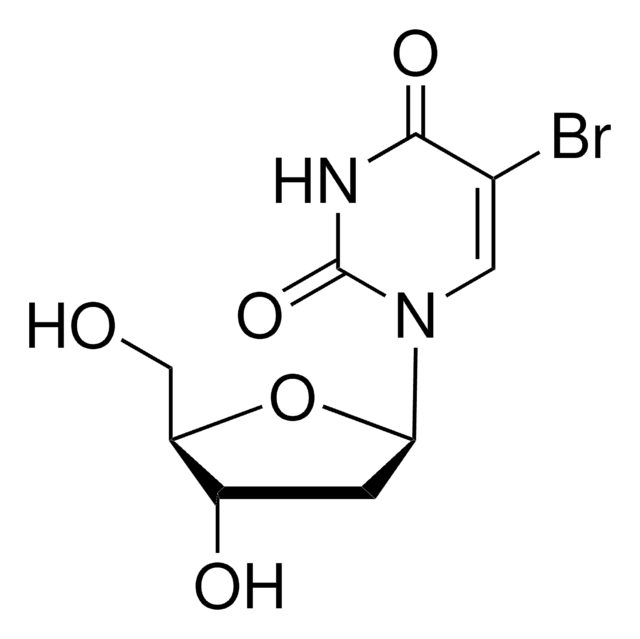
Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine is a monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine-5′-monophosphate.
Specificity
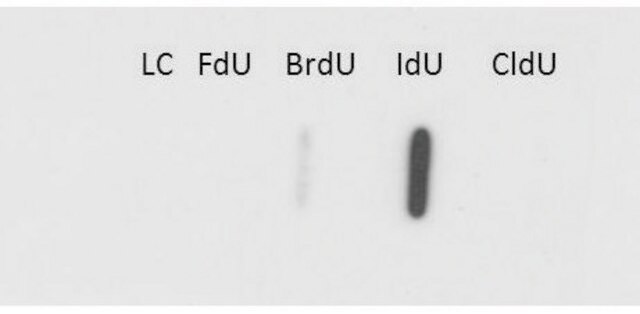
The antibody specifically binds to bromodeoxyuridine and crossreacts with iodouridine (10%). Anti-bromo-deoxyuridine does not crossreact with fluorodeoxy-uridine, nor with any endogenous cellular components such as thymidine or uridine.
Immunogen
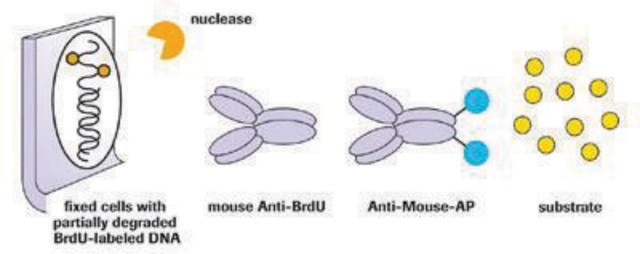
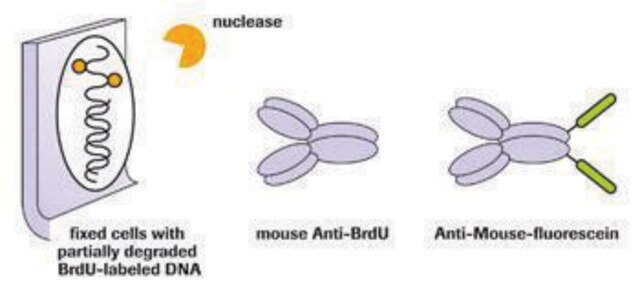
The epitope is apparently inside the DNA helix. DNA has to be denatured to ssDNA before antibody efficiently binds to DNA-BrdU.
Application
Anti-bromodeoxyuridine (Anti-BrdU) antibody is suitable for monitoring proliferating cells in blood, tissues, and tumors, as well as for determining BrdU incorporation on a single-cell level using:
- Flow cytometry
- Immunohistocytochemistry
- Cryosections
- Paraffin sections
Quality
The antibody is ≥90% pure as determined by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie-blue staining, and by HPLC.
Specifications
Preparation: BALB/c mice were immunized with a bromodeoxyuridine-bovine serum albumin conjugate. Lymphocytes isolated from the spleen were fused with Ag8.653 myeloma cells to create the BMC 9318 clone. The antibody was produced in ascites in BALB/c mice and purified by ion-exchange chromatography.
No. of tests: 250 (Flow cytometry)
No. of tests: 250 (Flow cytometry)
Physical form
Solution, stabilized with phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 0.2% (w/v) gelatin.
Preparation Note
Working concentration: Flow cytometry: 2 μg/ml (0.2 μg/100 μl/106 cells); Immunohistocytochemistry: 6 μg/ml
Working concentration of conjugate depends on application and substrate. Dilutions should be made in PBS (pH 7.4) containing 0.1% BSA to maintain stability of the antibody.
Working concentration of conjugate depends on application and substrate. Dilutions should be made in PBS (pH 7.4) containing 0.1% BSA to maintain stability of the antibody.
Analysis Note
Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine shows 10% cross reaction with iodo-deoxyuridine, but no cross reaction to fluoro-deoxyuridine.
No cross reaction to any endogenous thymidine or uridine.
Cross reactivity with 5-Br-UTP has not been tested but it is suggested that there is a good chance for reaction, because the only difference is an absent hydroxyl group on the ribose distal to the bromine substitution.
No cross reaction to any endogenous thymidine or uridine.
Cross reactivity with 5-Br-UTP has not been tested but it is suggested that there is a good chance for reaction, because the only difference is an absent hydroxyl group on the ribose distal to the bromine substitution.
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
No data available
flash_point_c
No data available
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Derek C Adams et al.
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology, 297(3), F809-F815 (2009-06-19)
Long-term pulse chase experiments previously identified a sizable population of BrdU-retaining cells within the renal papilla. The origin of these cells has been unclear, and in this work we test the hypothesis that they become quiescent early during the course
Wouter Laurentius Smit et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(41), 25560-25570 (2020-09-30)
Deregulated global mRNA translation is an emerging feature of cancer cells. Oncogenic transformation in colorectal cancer (CRC) is driven by mutations in APC, KRAS, SMAD4, and TP53, known as the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (ACS). Here we introduce each of these driver
Erika A Correll et al.
IBRO neuroscience reports, 10, 31-41 (2021-04-17)
It has been demonstrated that adult born granule cells are generated after traumatic brain injury (TBI). There is evidence that these newly generated neurons are aberrant and are poised to contribute to poor cognitive function after TBI. Yet, there is
Xuexiao Li et al.
Cell death discovery, 8(1), 323-323 (2022-07-17)
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are characterized by daunting genetic heterogeneity and a high risk of leukemic transformation, which presents great challenges for clinical treatment. To identify new chemicals for MDS, we screened a panel of FDA-approved drugs and verified the neutrophil
Victoria Sofía Berenice Wies Mancini et al.
Glia, 67(2), 291-308 (2018-11-21)
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is one of the most common causes of progressive disability affecting young people with very few therapeutic options available for its progressive forms. Its pathophysiology involves demyelination and neurodegeneration apparently driven by microglial activation, which is physiologically
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service