11175041910
Roche
DIG Nucleic Acid Detection Kit
sufficient for 40 blots (10 cm x 10 cm each), kit of 1 (5 components), suitable for hybridization, suitable for Northern blotting
Synonym(s):
DIG system
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 40 blots (10 cm x 10 cm each)
Quality Level
packaging
kit of 1 (5 components)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
greener alternative product characteristics
Designing Safer Chemicals
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
technique(s)
Northern blotting: suitable
Southern blotting: suitable
hybridization: suitable
greener alternative category
, Aligned
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Application
- Southern blots
- Northern blots
- Other nucleic acid blotting applications
- In situ hybridization applications
- Southern blots
- Northern blots
- Other nucleic acid blotting applications
- In situ hybridization applications
Features and Benefits
Packaging
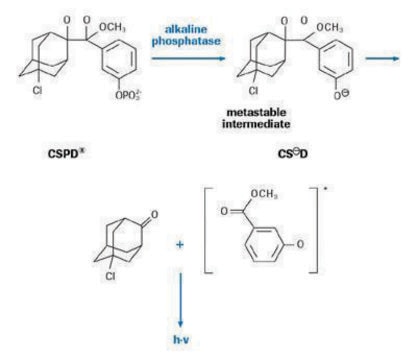
Principle
Preparation Note
Working concentration of conjugate depends on application and substrate.
Storage conditions (working solution):
- Anti-Digoxigenin-AP Conjugate (vial 3): 2 to 8 °C, it is stable for 12 months at this temperature
- NBT/BCIP (vial 4): 2 to 8 °C, stable
Note: During shipment of the kit on dry ice, a precipitate may occur which is dissolved by briefly warming to 37 °C - The blocking reagent (vial 5) is stable for 36 months and can be stored dry at 4 to 8 °C.
- Autoclaved stock solution can be stored for several days to a week either unopened at 15 to 25 °C or at 4 to 8 °C after opening. Alternatively, it can be stored in aliquots at -15 to -25 °C for up to 6 months.
Kit Components Only
- DIG-labeled Control DNA 5 µg/ml
- DNA Dilution Buffer, [50 μg/ml] fish sperm DNA
- Anti-Digoxigenin-AP Conjugate antibody 750 U/ml
- NBT/BCIP, 50x stock solution 50x concentrated
- Blocking Reagent
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Digoxigenin (DIG) labeling methods and kits for DNA and RNA DIG probes, random primed DNA labeling, nick translation labeling, 5’ and 3’ oligonucleotide end-labeling.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service