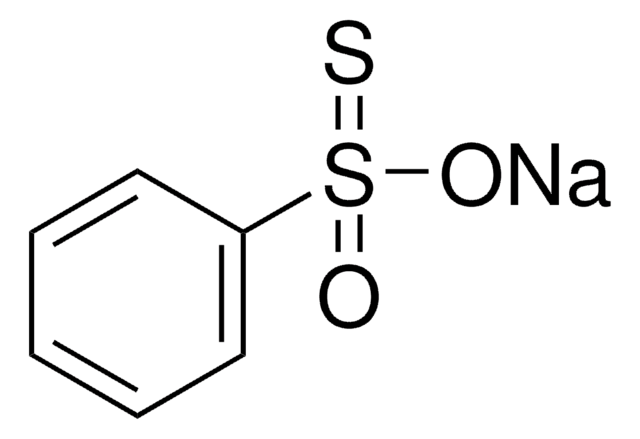
64306
S-Methyl methanethiosulfonate
purum, ≥98.0% (GC)
Synonym(s):
S-Methyl thiomethanesulfonate, MMTS
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
purum
Quality Level
assay
≥98.0% (GC)
refractive index
n20/D 1.513 (lit.)
n20/D 1.513
bp
69-71 °C/0.4 mmHg (lit.)
solubility
chloroform: 750mg + 5 ml Chloroform mg/mL, colorless to light greenish-yellow
density
1.337 g/mL at 20 °C
1.337 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CSS(C)(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C2H6O2S2/c1-5-6(2,3)4/h1-2H3
InChI key
XYONNSVDNIRXKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Modification of Thiol Enzymes: S-methyl methanethiosulfonate (MMTS) offers a unique method for the modification of thiol enzymes and redox-regulated proteins, providing potential applications in biochemical research focused on enzyme regulation and redox biology (Makarov et al., 2019).
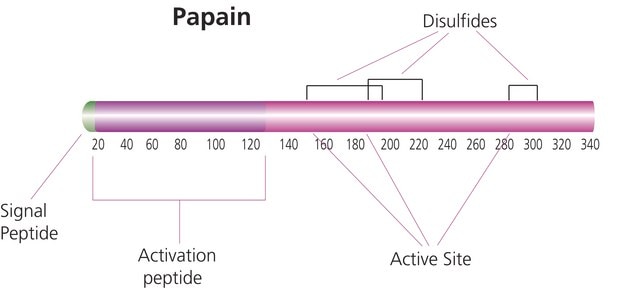
- Sensor Development for Protease Activity: S-methyl methanethiosulfonate is used as a blocking reagent on the structural transitions of papain-like cysteine proteases, which supports its utility in sensor development, allowing for the detection and analysis of protease activity in various biological processes (Markovic et al., 2023).
- Agricultural Pathogen Control: Research evaluating S-methyl methanethiosulfonate as a late blight inhibitor highlights its potential as a broad-range toxin against plant pathogens, suggesting applications in agriculture for the management of crop diseases (Joller et al., 2020).
Caution
Other Notes
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
closed cup
flash_point_c
closed cup
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service