89922
Elemental Impurities according to ICH Q3D parenteral, Standard 2
TraceCERT®, (in 10% hydrochloric acid), applicable for testing acc. to USP<232>, Ph.Eur. Gen. Chapter 5.20
Synonym(s):
ICH Q3D Elemental Impurity Standard 2
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
certified reference material
TraceCERT®
Quality Level
agency
according to ICH Q3D
according to Ph. Eur.
according to USP
product line
TraceCERT®
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
composition
Au, 100 mg/L
Ir, 10 mg/L
Os, 10 mg/L
Pd, 10 mg/L
Pt, 10 mg/L
Rh, 10 mg/L
Ru, 10 mg/L
concentration
(in 10% hydrochloric acid)
technique(s)
ICP: suitable
format
multi-component solution
Related Categories
General description
Certified content incl. uncertainty and expiry date are given on the certificate.
Download your certificate at: http://www.sigma-aldrich.com.
Application
<li><strong>Determination of ICH-Q3D Elemental Impurity Leachables in Glass Vials:</strong> This study applies inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to assess ICH-Q3D elemental impurity leachables in glass vials used for parenteral applications, providing a crucial methodology for ensuring compliance with pharmaceutical heavy metal analysis standards (Breckenridge et al., 2023).</li>
<li><strong>Application of ICH Guidelines for Assessment and Control of Elemental Impurities in Parecoxib Sodium:</strong> Utilizing graphite-digestion and ICP-MS, this research conforms to the ICH Q3D guidelines for evaluating elemental impurities in parecoxib sodium, highlighting a robust approach for elemental impurity analysis in injectable pharmaceuticals (Hao et al., 2022).</li>
<li><strong>Risk-Based Approach to Evaluate and Control Elemental Impurities in Therapeutic Proteins:</strong> This study introduces a risk-based strategy for the assessment and control of elemental impurities in therapeutic proteins, which aligns with the requirements of USP <232> <233> compliance and aids in the development of safer parenteral medications (Luo et al., 2020).</li>
<li><strong>Assessment of Extractable Elements from Elastomers:</strong> Investigating the potential for elemental impurities to leach from elastomers, this research is vital for the risk assessment of elemental contaminants in parenteral formulations, ensuring safety and compliance with ICH Q3D standards (Paskiet et al., 2019).</li>
</ul>
Preparation Note
Legal Information
related product
signalword
Warning
hcodes
pcodes
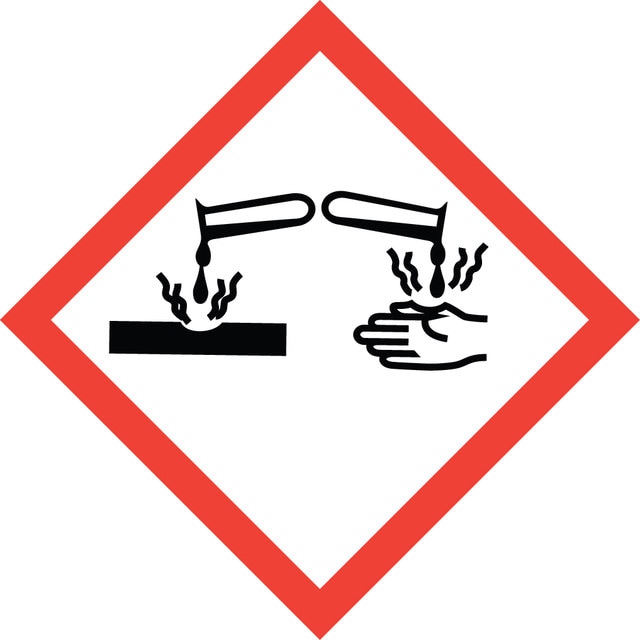
Hazard Classifications
Met. Corr. 1
wgk_germany
WGK 1
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Elemental impurities in drug products pose a risk to patient health due to toxicological effects, and their levels should be controlled within acceptable limits. Find analytical methods and materials for impurity assessment.
In 2009, the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) proposed the development of a new harmonized guideline to provide a global policy for limiting metal impurities in drug products and ingredients. This approach provides clear regulatory guidance on specification limits for elemental impurities worldwide and logically should have an impact on the work of the national regulatory bodies in having transparent and comparable results.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service