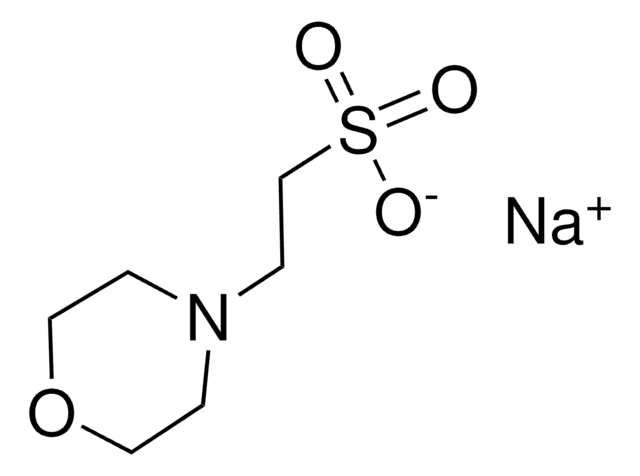
69892
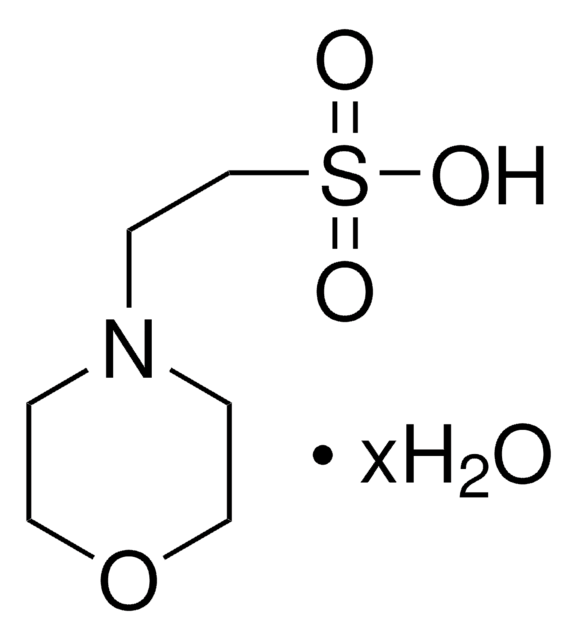
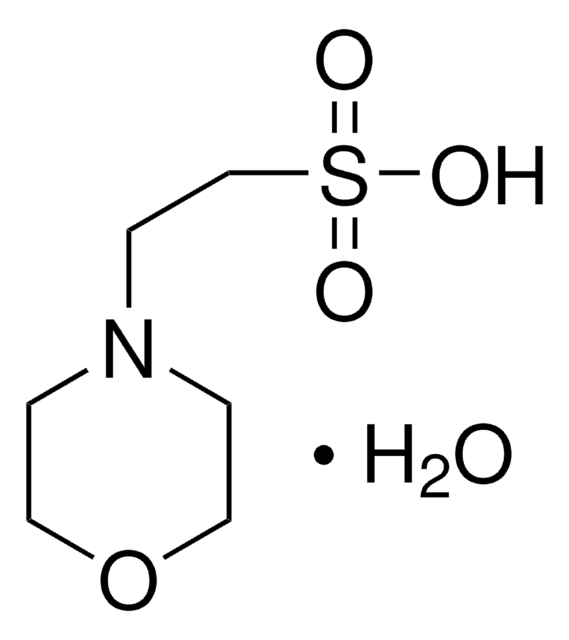
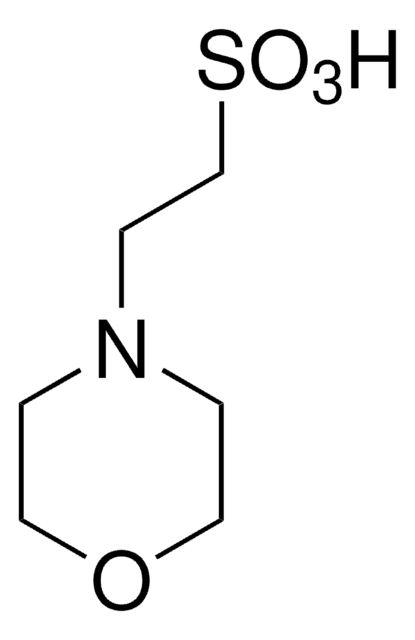
MES monohydrate
BioXtra, ≥99.0% (T)
Synonym(s):
2-(4-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid, 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid, Morpholine-4-ethanesulfonic acid hydrate, 2-(N-Morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid, 4-Morpholineethanesulfonic acid monohydrate
About This Item
Recommended Products
product line
BioXtra
Quality Level
assay
≥99.0% (T)
form
powder or crystals
useful pH range
5.5-6.7
pKa (25 °C)
6.1
mp
>300 °C (lit.)
solubility
H2O: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear
density
10.66 g/mL
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 mg/kg
cation traces
Ca: ≤50 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Na: ≤50 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
application(s)
agriculture
diagnostic assay manufacturing
general analytical
microbiology
foreign activity
DNase, none detected
NICKase, none detected
RNase, none detected
protease, none detected
SMILES string
O.OS(=O)(=O)CCN1CCOCC1
InChI
1S/C6H13NO4S.H2O/c8-12(9,10)6-3-7-1-4-11-5-2-7;/h1-6H2,(H,8,9,10);1H2
InChI key
MIIIXQJBDGSIKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- to adjust the pH of the growth medium, facilitating gene expression analyses aimed at understanding the molecular mechanisms
- in the fixation and imaging of cellular components, enabling the study of hypotonic stress′s physiological effects on cell structure and function through Super-Resolution and Live-Cell Microscopy
- to adjust the pH of the growth medium to 5.5-7.0 in an in vitro cell wall stress assay
- as a buffering agent to stabilize enzymatic solutions
- as a component of PAGE running buffer
Features and Benefits
- Suitable for Biochemical and Cell Biology Research
- Tested for the presence of anionic and cationic traces
- Tested to confirm low levels of heavy metal contamination, ensuring suitability for various applications
- Effective Buffering from pH 5.5-6.7 (25 °C) with a pKa of 6.1 (25 °C)
Preparation Note
Other Notes
Sterilization: Sterilization should be by filteration through 0.2μM filters. Autoclaving is not recommended by any sulfonic acid buffers. If buffers must be nuclease-free, it is best to treat the water, then add the buffer solids after autoclaving. When MES solutions are autoclaved, they turn yellow (although pH does not change measurably. The identity of the yellow breakdown product is unkown.
wgk_germany
WGK 1
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service