C1235
Cholesterol Oxidase microbial
recombinant, lyophilized powder, ≥10 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Cholesterol: oxygen oxidoreductase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥10 units/mg protein
mol wt
55 kDa
solubility
50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0: soluble
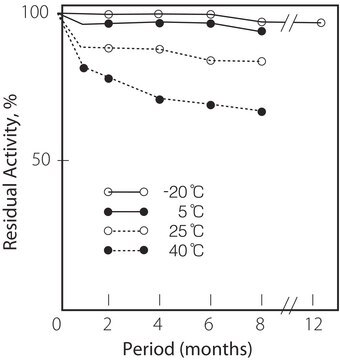
storage temp.
−20°C
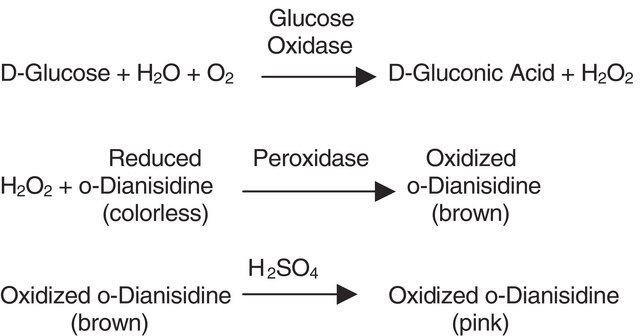
Application
Cholesterol oxidase is used to determine serum cholesterol. The enzyme also finds application in the microanalysis of steroids in food samples and in distinguishing 3-ketosteroids from 3b-hydroxysteroids. Transgenic plants expressing cholesterol oxidase are being investigated in the fight against the cotton boll weevil. CHOD has also been used as a molecular probe to elucidate cellular membrane structures.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cholesterol oxidase (CHOD) is a monomeric flavoprotein containing FAD that catalyzes the first step in cholesterol catabolism. This bifunctional enzyme oxidizes cholesterol to cholest-5-en-3-one in an FAD-requiring step. This is subsequently isomerized to cholest-4-en-3-one with the release of H2O2. Optimum pH of the enzyme is 7.0. Hg2+, Ag+, ionic detergents inhibit the enzyme activity.
Unit Definition
One unit will convert 1.0 μmol of cholesterol to 4-cholesten-3-one per minute at 37 °C and pH 7.0 in a peroxidase linked system.
Preparation Note
Dissolves in cold 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. Solution is to be prepared just before use.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Bruno M Castro et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 284(34), 22978-22987 (2009-06-13)
A uniquely sensitive method for ceramide domain detection allowed us to study in detail cholesterol-ceramide interactions in lipid bilayers with low (physiological) ceramide concentrations, ranging from low or no cholesterol (a situation similar to intracellular membranes, such as endoplasmic reticulum)
Christophe A Marquette et al.
Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 390(1), 155-168 (2007-10-03)
The present review draws a general picture of the bioanalytical applications of electro-chemiluminescent reactions (ECL). Only the two main ECL reactions-i.e. the luminol-based and Ru(bpy)(3)(2+)-based reactions-are considered for application in the fields of enzyme biosensors, immunochemical biosensors, DNA biosensors, and
Effect of cholesterol concentration on organization of viral and vesicle membranes. Probed by accessibility to cholesterol oxidase.
R Pal et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 255(12), 5802-5806 (1980-06-25)
D R Corbin et al.
Plant physiology, 126(3), 1116-1128 (2001-07-18)
Cholesterol oxidase represents a novel type of insecticidal protein with potent activity against the cotton boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis grandis Boheman). We transformed tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants with the cholesterol oxidase choM gene and expressed cytosolic and chloroplast-targeted versions of
Mitsutoshi Toyama et al.
Protein engineering, 15(6), 477-484 (2002-06-26)
Despite the structural similarities between cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces and that from Brevibacterium, both enzymes exhibit different characteristics, such as catalytic activity, optimum pH and temperature. In attempts to define the molecular basis of differences in catalytic activity or stability
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service