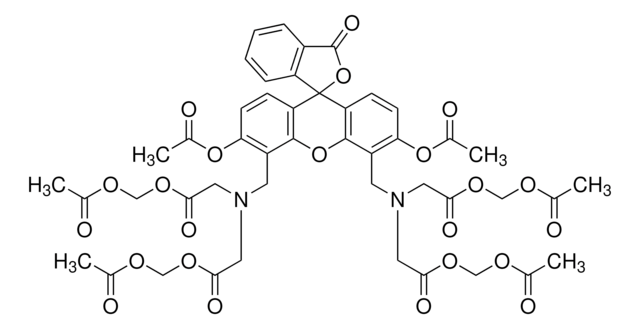
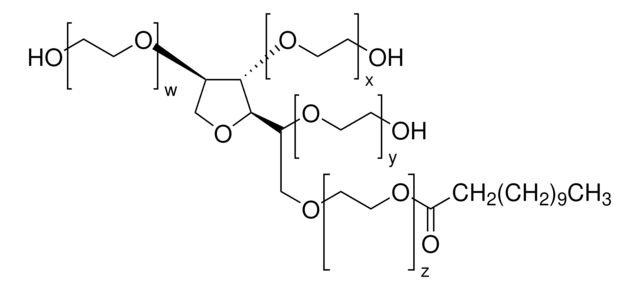
CS0340
Dihydrofolate Reductase Assay Kit
1 kit sufficient for 50-100 tests
Synonym(s):
DHFR Assay Kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
usage
kit sufficient for 50-100 tests
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... DHFR(1719)
Related Categories
Application
Dihydrofolic acid+NADPH+H+ ↔ Tetrahydrofolic acid+NADP+
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
- Quick and simple method.
- The kit contains all the reagents required for a colorimetric assay of DHFR activity in cell lysates, tissue homogenates, or column fractions of purified enzyme.
- The kit includes a purified enzyme for use as a positive control and screening of DHFR inhibitors.
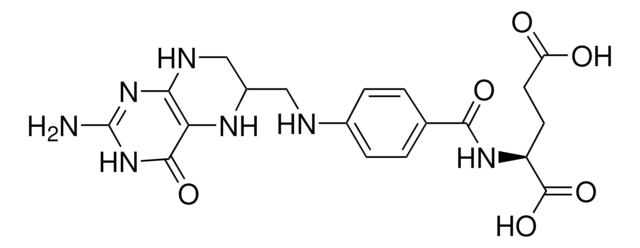
- The kit includes methotrexate (MTX), a prokaryotic and eukaryotic DHFR specific inhibitor, which exhibits anti-tumor activities.
- The kit was tested on A431, NIH-3T3, and CHO cell lines, rat liver, kidney, brain, and skeletal muscle tissue extracts, and recombinant DHFR.
Kit Components Only
- Assay Buffer 10x for DHFR 30 mL
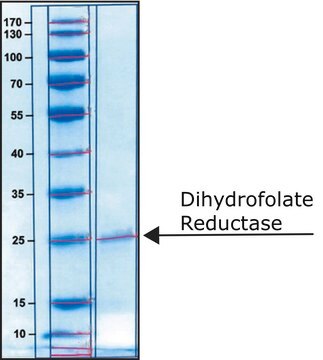
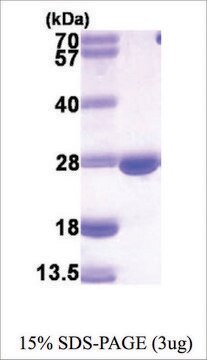
- Dihydrofolate Reductase (DHFR) human .1 U
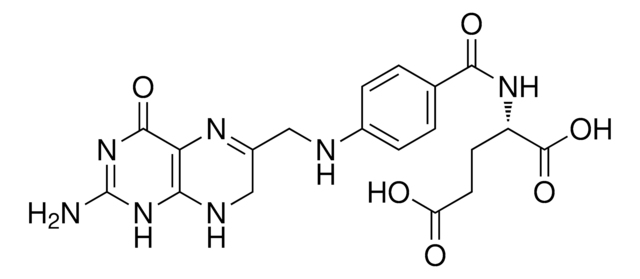
- Dihydrofolic acid (DHFR substrate) 3 x 10
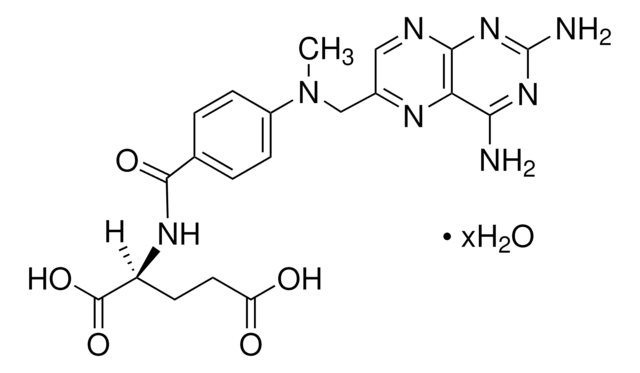
- Amethopterin (+)(methotrexate, MTX)
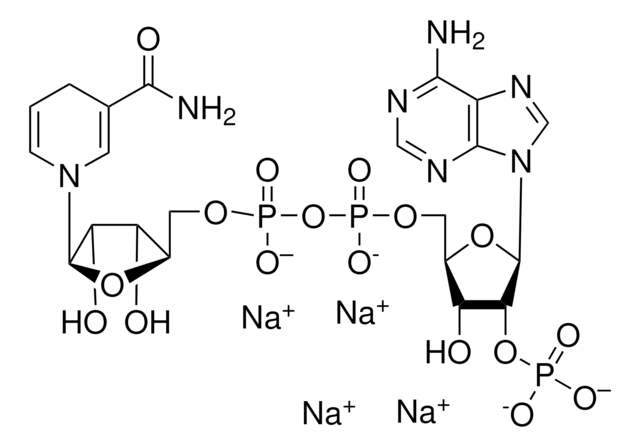
(DHFR inhibitor) 2 x 10 - NADPH (β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced tetrasodium salt) 25 mg
signalword
Danger
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Repr. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
6.1C - Combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
This article reviews some of our newest and most innovative technologies and their specific applications toward cancer research. It describes how complex the disease of cancer is, and how difficult it is to identify one topic that is completely unrelated to any other.
This issue of Biofiles reviews some of our newest and most innovative technologies and their specific applications toward cancer research. In preparing this issue of Biofiles, one is reminded how complex the disease of cancer is, and how difficult it is to identify one topic that is completely unrelated to any other.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service