D2141
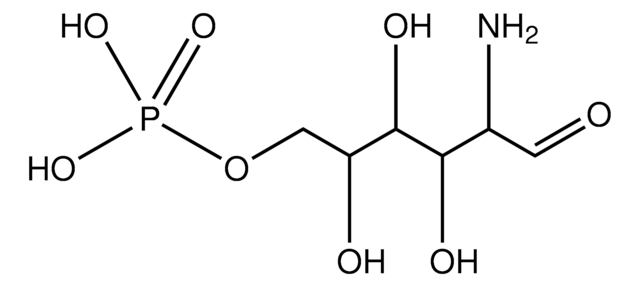
6-Diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine
crystalline
Synonym(s):
(S)-2-Amino-6-diazo-5-oxocaproic acid, DON
About This Item
Recommended Products
assay
>95% (TLC)
Quality Level
form
crystalline
technique(s)
ligand binding assay: suitable
color
light yellow
mp
145 °C
antibiotic activity spectrum
neoplastics
mode of action
enzyme | inhibits
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
N[C@@H](CCC(=O)C=[N+]=[N-])C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H9N3O3/c7-5(6(11)12)2-1-4(10)3-9-8/h3,5H,1-2,7H2,(H,11,12)/t5-/m0/s1
InChI key
YCWQAMGASJSUIP-YFKPBYRVSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Storage Class
6.1C - Combustible, acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about how proliferatively active cells require both a source of carbon and of nitrogen for the synthesis of macromolecules. Although a large proportion of tumor cells utilize aerobic glycolysis and shunt metabolites away from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, many tumor cells exhibit increased mitochondrial activity.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service