F0425
Anti-Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-3, Cytoplasmic antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-FGFR-3
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
antigen 110-120 kDa (doublet)
species reactivity
human
technique(s)
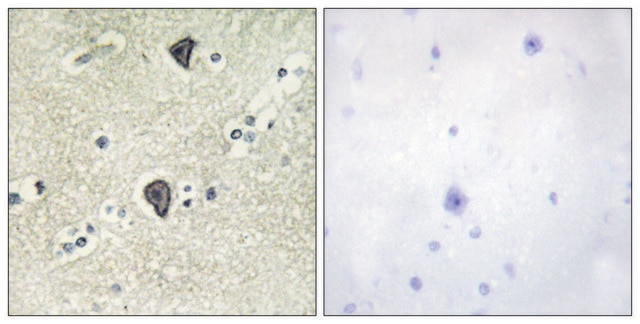
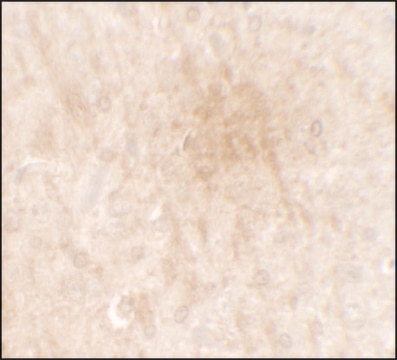
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:250 using Trypsin-digested, human and animal tissue sections
western blot: 1:1,000 using whole cell extract of transfected 293T cells expressing recombinant human FGFR-3
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... FGFR3(2261)
Related Categories
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Immunohistochemistry (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service