F5766
Monoclonal Anti-Folic Acid antibody produced in mouse
clone VP-52, ascites fluid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
ascites fluid
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
VP-52, monoclonal
contains
15 mM sodium azide
technique(s)
indirect ELISA: 1:500
isotype
IgG2b
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Related Categories
General description
Monoclonal Anti-Folic Acid (mouse IgG2b isotype) is derived from the hybridoma produced from the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes of an immunized mouse. The normal range for folate in serum is 3-13 ng/ml.
Specificity
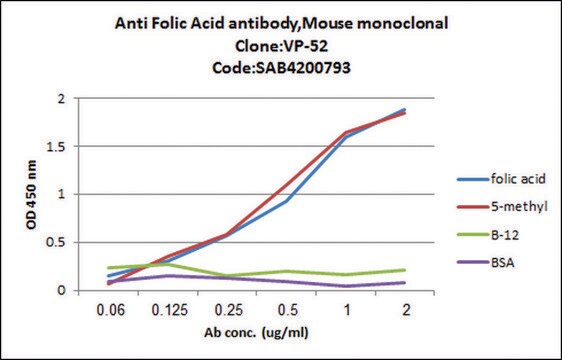
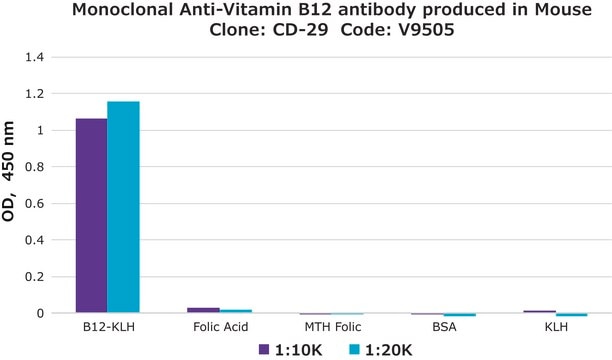
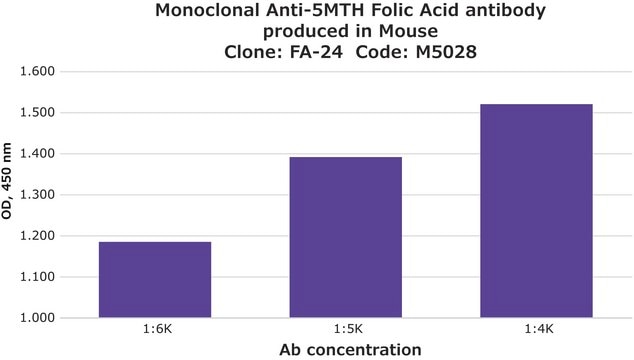
Monoclonal Anti-Folic Acid antibody binds specifically to folate and detects an epitope present on both folic acid and its biologically active analog 5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid (5MTHFA). The product reacts with free folate, folate conjugated to a carrier such as KLH or BSA, and folic acid in human plasma or serum bound to the endogenous Folate Binder. The antibody does not cross-react with tetrahydrofolic acid, folinic acid or dihydrofolic acid.
Immunogen
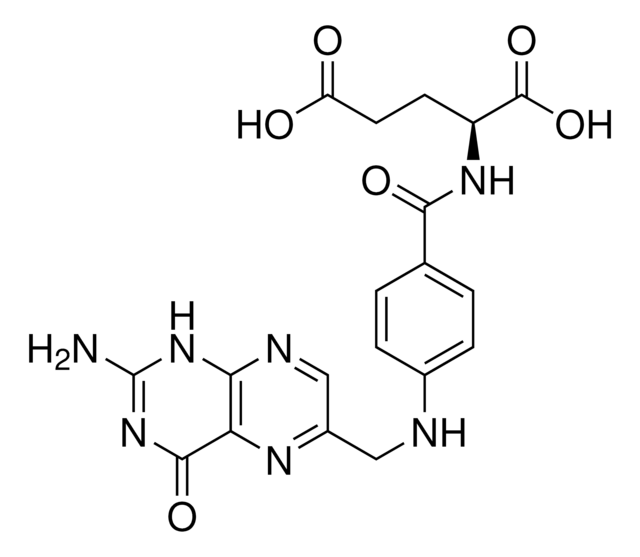
5-Methyltetrahydrofolic acid (5MTHFA) conjugated to KLH
Application
Monoclonal Anti-Folic Acid antibody is suitable for use in western blot (diluted 1:1000).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Folic acid (folate) is a vitamin that regulates one-carbon transfer during the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. Methionine is a precursor of S-adenosylmethionine, which is the main methyl donor for methylation reactions. Thus, folic acid is essential for regulation of DNA methylations and for epigenetic modifications that modulate gene expression. Folate deficiency has been associated with a wide range of disorders including colorectal cancers, depression, neural tube defects and cerebral dysfunctions
Folic acid is essential for normal growth of mammalian cells. Folic acid deficiencies are common in pregnant women, alcoholics, those whose diets do not include raw fruits and vegetables, and people with structural or functional damage to the small intestine. Vitamin B12 and folic acid are metabolically interrelated.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Young-In Kim
Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology, 13(4), 511-519 (2004-04-07)
Epidemiological, clinical, and animal studies collectively indicate that dietary folate intake and blood folate levels are inversely associated with colorectal cancer risk. Folate plays an essential role in one-carbon transfer involving remethylation of homocysteine to methionine, which is a precursor
Folic acid: A positive influence on periodontal tissues during health and disease
George JP, et al.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED MULTIDISCIPLINARY RESEARCH, 2(3), 145-145 (2013)
Keith Hyland et al.
Journal of inherited metabolic disease, 33(5), 563-570 (2010-07-30)
Cerebral folate deficiency (CFD) is defined as any neurological syndrome associated with a low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentration of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5MTHF) in the presence of normal peripheral folate status. CFD has a wide clinical presentation, with reported signs and symptoms
Periconceptional folate deficiency and implications in neural tube defects.
Safi, J., et al.
Journal of Pregnancy, doi: 10-doi: 10 (2012)
Clinical utility of serum folate measurement in tertiary care patients: Argument for revising reference range for serum folate from 3.0 ng/mL to 13.0 ng/mL
Singh G, et al.
practical laboratory medicine, 1, 35-35 (2015)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service