H9914
HIS-Select® Nickel Magnetic Agarose Beads
Synonym(s):
nickel charged magnetic beaded agarose
About This Item
Recommended Products
conjugate
magnetic beads
Quality Level
form
suspension
shelf life
2 yr (Unopened product)
matrix
6% beaded magnetic agarose
capacity
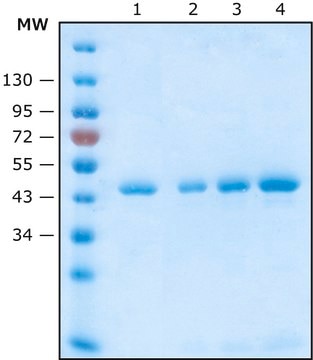
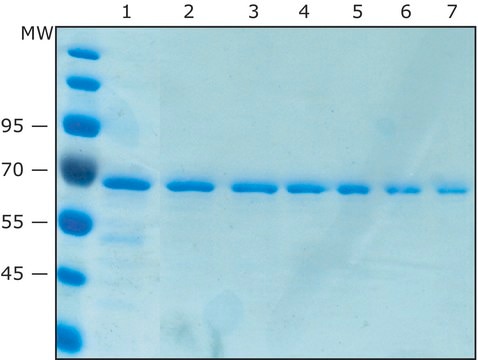
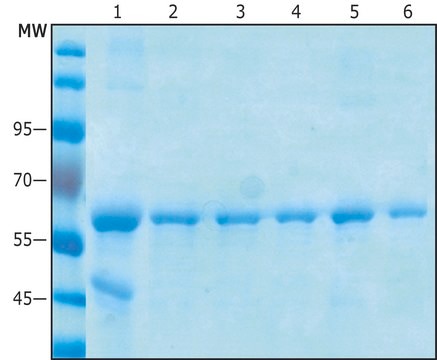
≥15 mg/mL binding capacity
storage temp.
2-8°C
Related Categories
General description
Application
Physical form
Legal Information
related product
signalword
Danger
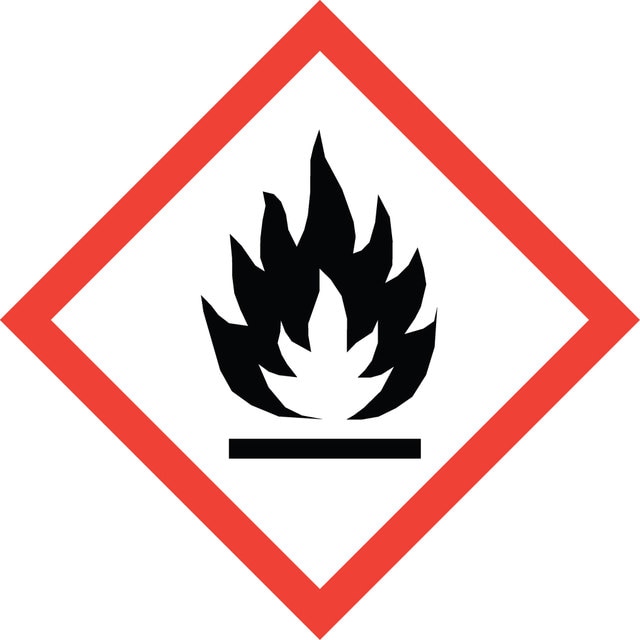
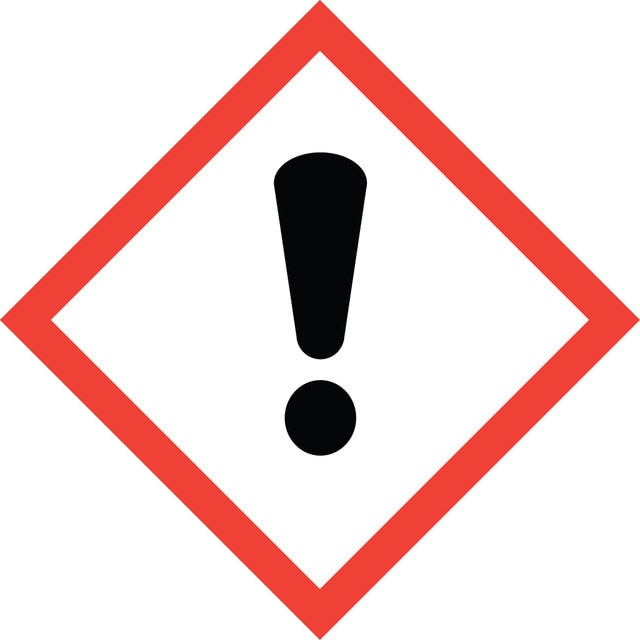
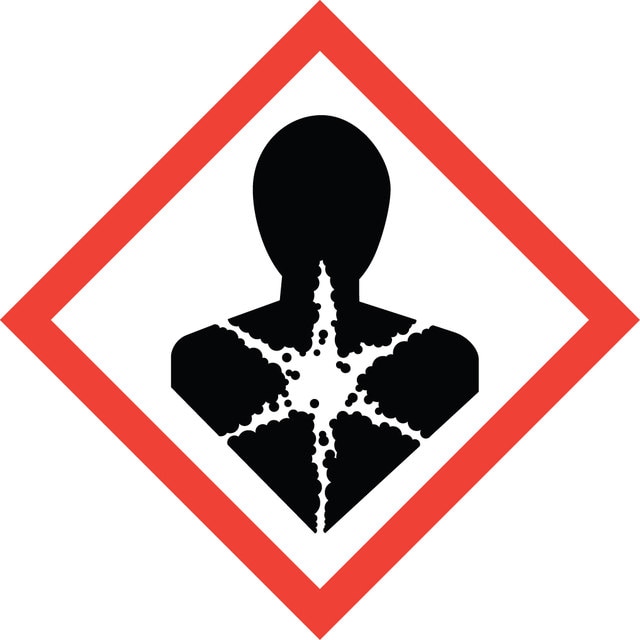
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Carc. 1B - Flam. Liq. 3 - Repr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2
target_organs
Respiratory Tract
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
86.0 °F
flash_point_c
30 °C
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Related Content
Protein purification techniques, reagents, and protocols for purifying recombinant proteins using methods including, ion-exchange, size-exclusion, and protein affinity chromatography.
Protein expression technologies for expressing recombinant proteins in E. coli, insect, yeast, and mammalian expression systems for fundamental research and the support of therapeutics and vaccine production.
Pull-down assays, reagents, and protocols for investigating in vitro protein-protein interactions using affinity or GST pull-down, tandem affinity purification (TAP), and co-immunoprecipitation methods.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service