NPT01
NeuroPorter™ Transfection Kit
Lipid formulation for nucleic acid transfections in neuronal and glial cells
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
for molecular biology
Quality Level
form
dried film
usage
kit sufficient for 75-200 transfections
availability
available only in USA, Canada and EU
technique(s)
transfection: suitable
storage temp.
2-8°C
Related Categories
General description
Application
- C6 glioma (human)
- Cortical neurons (rat primary)
- Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) cells (rat)
- NT2 neurons(human precursor cells)
- NT neurons (human differentiated cells)
- Subventricular Zone (SVZ) cells (mouse)
- White matter cells (mouse)
Features and Benefits
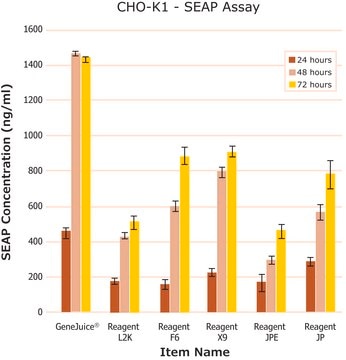
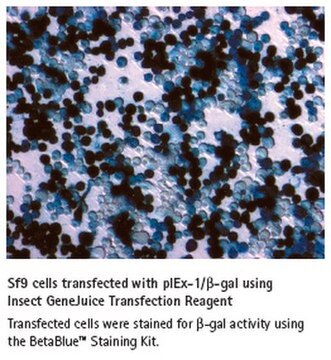
- Optimized for primary neurons, glial cells, and cultured neural cell lines
- Very low toxicity with no neuro-degeneration or dendrite withdrawal
- Efficient DNA delivery primary neurons, glial cells, and cultured neural cell lines
- Fast and easy to use compared to other methods
- Compatible with both serum and serum-free transfection protocols
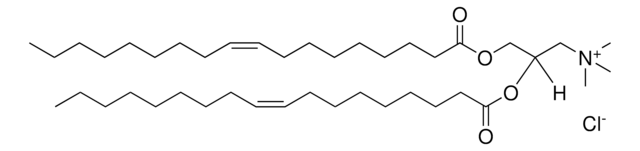
Components
1.5 mL Hydration Buffer H9036
7.5 mL DNA Diluent D1941
Caution
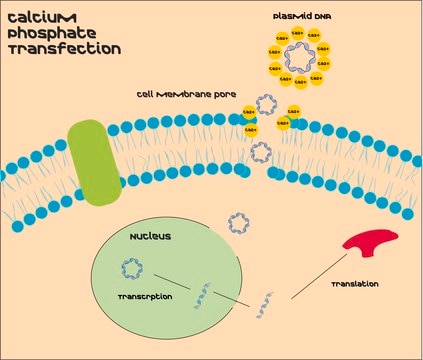
Principle
Legal Information
related product
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Transfection is the introduction of DNA, RNA, or proteins into eukaryotic cells and is used in research to study and modulate gene expression. Thus, transfection techniques and protocols serve as an analytical tool that facilitates the characterization of genetic functions, protein synthesis, cell growth and development.
This brief webinar provides an overview of what transfection is and the methods that are used to introduce DNA or RNA into eukaryotic cells.
Related Content
Browse our convenient transfection reagent selection guide to match the best reagent for your specific cell line and application needs.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service