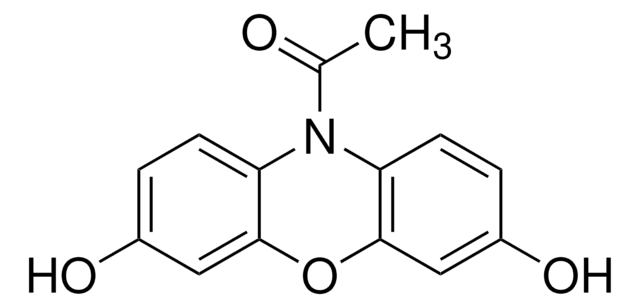
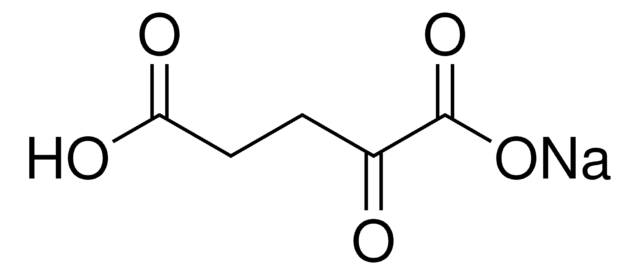
P4591
Pyruvate Oxidase from microorganisms
lyophilized powder, ≥1.5 U/mg
Synonym(s):
Pyruvate:oxygen oxidoreductase (phosphorylating)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(5)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Application
Pyruvate Oxidase (PoxB) converts pyruvate directly to acetate and CO2. It is used to study pyruvate metabolism. It is used to study aerobic metabolism of bacterium, such as Lactobacillus plantarumand Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pyruvate Oxidase is used for enzymatic determination of pyruvate, GOT, and GPT in clinical analysis.
Pyruvate Oxidase from microorganisms has been used in the Amplex Red-based fluorescence assay for pyruvate. It has also been used in developing near real-time continuous detection system for pyruvate.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pyruvate Oxidase consists of four subunits with identical molecular weights. PoxB reacts with certain aldehydes and phosphate can be replaced by arsenate. Oxygen as well as several artificial compounds can function as electron acceptors. Pyruvate Oxidase is activated by phospholipids as well as monomeric and micellar amphiphiles.
Pyruvate Oxidase oxidises pyruvate to form acetate, hydrogen peroxide and carbondioxide. Pyruvate oxidase requires flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and magnesium as cofactors for its catalytic activity. Pyruvate oxidase is activated by the cofactor thiamine.
Physical properties
Isoelectric point : 4.3
Michaelis constant : 3.4 X 10-4M (Pyruvate)
Inhibitors : Fe++,Zn++,Cu++,Ag+,Hg++
Optimum pH : 5.7
Optimum temperature : 65oC
pH Stability : pH 5.7 - 6.5 (25oC, 20hr)
Thermal stability : below 45oC (pH 6.0, 15min)
Michaelis constant : 3.4 X 10-4M (Pyruvate)
Inhibitors : Fe++,Zn++,Cu++,Ag+,Hg++
Optimum pH : 5.7
Optimum temperature : 65oC
pH Stability : pH 5.7 - 6.5 (25oC, 20hr)
Thermal stability : below 45oC (pH 6.0, 15min)
Unit Definition
One unit will produce 1.0 μmole of H2O2 per min during the conversion of pyruvate and phosphate to acetylphosphate and CO2 at pH 5.7 at 37 °C.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder containing FAD and sugar as stabilizer
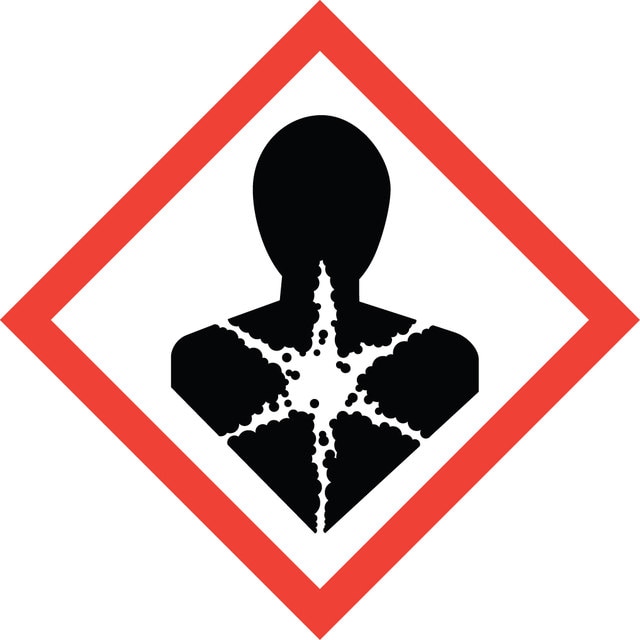
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Multiplexed and fully automated detection of metabolic biomarkers using microdialysis probe
Das C, et al.
Sensors and Actuators B, Chemical, 238, 633-640 (2017)
A sensitive fluorimetric assay for pyruvate
Zhu A, et al.
Analytical Biochemistry, 396(1), 146-151 (2010)
Lan-yan Zheng et al.
International journal of oral science, 3(2), 82-89 (2011-04-13)
The objective of this study was to characterize the oxygen dependent regulation of pyruvate oxidase (SpxB) gene expression and protein production in Streptococcus sanguinis (S. sanguinis). SpxB is responsible for the generation of growth-inhibiting amounts of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) able
Amit Priyadarshi et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 380(4), 797-801 (2009-04-03)
MenD (2-succinyl-5-enolpyruvyl-6-hydroxy-3-cyclohexadiene-1-carboxylate) synthase belongs to the superfamily of thiamin diphosphate-dependent decarboxylases, which converts isochorismate and 2-oxoglutarate to SHCHC, pyruvate, and carbon dioxide. Here, we report the first crystal structure of apo-MenD from Escherichia coli determined in tetragonal crystal form. The
Rachel Benisty et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1801(9), 1098-1104 (2010-07-06)
FabF elongation condensing enzyme is a critical factor in determining the spectrum of products produced by the FASII pathway. Its active site contains a critical cysteine-thiol residue, which is a plausible target for oxidation by H2O2. Streptococcus pneumoniae produces exceptionally
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service