General description
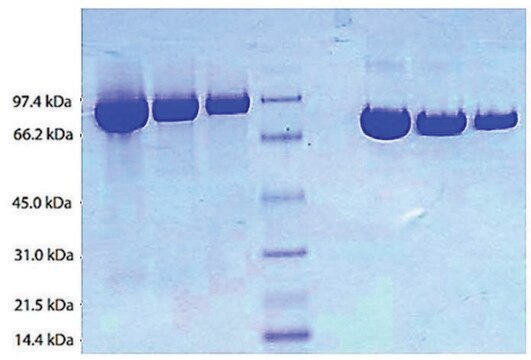
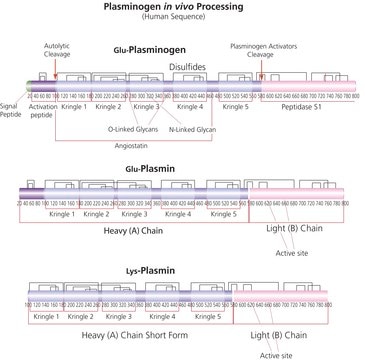
The plasminogen (PLG) gene is mapped to human chromosome 6q26. Plasminogen protein has a molecular weight of ?90kDa. It is composed of Pan-apple domain at the N-terminal, five kringle domains and serine protease domain at its C-terminal.
Application
Plasminogen is a single-chain glycoprotein found in human plasma and extracellular fluid. Certain activators, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), convert plasminogen to its active form, plasmin. Plasminogen has been used to study its conversion into plasmin.
The enzyme from Sigma has been used to examine the ability of plasminogen in nasal secretion to promote S. aureus surface colonization. It has been used to assess the binding of recombinant OspC protein to plasminogen using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. It has also been used to screen FITC-labeled S. pneumoniae for protein interaction by solid-phase assay. In this assay; a well was coated with plasminogen and incubated with FITC-labeled bacteria.The fluorescence signal was read in a fluorimeter.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Plasminogen is the inactive precursor of the protease plasmin. Plasminogen is activated by the action of either tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which primarily activates the fibrinolytic (thrombolytic) activity of plasmin, or urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), which is associated with extracellular matrix remodeling and cell migration. Plasmin cleaves fibrin/fibrinogen and blood coagulation factors V/Va and VIII/VIIIa. It activates matrix metalloproteinases by cleaving the inactive proenzymes. It is also involved in the activation of some growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β).
Physical properties
Native-intact human plasminogen is a 791 amino acid glyco-protein with as many as 24 disulfide bonds. Plasminogen contains a single N-linked sialylated biantennary glycan. The two O-glycans possess a Gal β-1-3GalNAc core which are α-2-3 sialylated at the terminal Gal. An additional disialylated form has a second sialic acid residue with an α-2-6 linkage to GalNAc. Mono- and disialylated forms occur at a molar ratio of 80:20 in human plasminogen.
Unit Definition
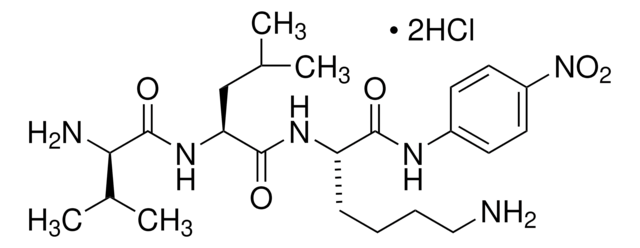
One unit will produce one micromole of p-Nitroanilide from D-Val-Leu-Lys-p-Nitroanilide per minute at pH 7.5 at 37 °C. Activity is determined after activation to plasmin with urokinase.
Reconstitution
Solutions should be stored in buffer containing 20 mM lysine at neutral pH. The protein should be as concentrated as possible. Frozen in aliquots at −20 °C, it should be stable for several weeks.
Analysis Note
ε-Aminocaproic acid free
Plasma from each donor has been tested and found negative for antibody to HIV-1/HIV-2, antibody to HCV and HbSAg.
Disclaimer
RESEARCH USE ONLY. This product is regulated in France when intended to be used for scientific purposes, including for import and export activities (Article L 1211-1 paragraph 2 of the Public Health Code). The purchaser (i.e. enduser) is required to obtain an import authorization from the France Ministry of Research referred in the Article L1245-5-1 II. of Public Health Code. By ordering this product, you are confirming that you have obtained the proper import authorization.