SAB1401190
Anti-IAPP antibody produced in rabbit
purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
AMYLIN, DAP, IAP
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.43
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
species reactivity
human
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... IAPP(3375)
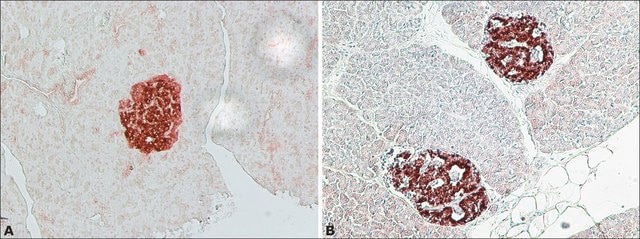
General description
Islet, or insulinoma, amyloid polypeptide is commonly found in pancreatic islets of patients suffering diabetes mellitus type II, or harboring an insulinoma. While the assosciation of amylin with the development of type II diabetes has been known for some time, a direct causative role for amylin has been harder to establish. Studies suggest that amylin, like the related beta-amyloid (Abeta) associated with Alzheimer′s disease, can induce apoptotic cell-death in particular cultured cells, an effect that may be relevant to the development of type II diabetes. (provided by RefSeq)
Immunogen
IAPP (NP_000406.1, 1 a.a. ~ 89 a.a) full-length human protein.
Sequence
MGILKLQVFLIVLSVALNHLKATPIESHQVEKRKCNTATCATQRLANFLVHSSNNFGAILSSTNVGSNTYGKRNAVEVLKREPLNYLPL
Sequence
MGILKLQVFLIVLSVALNHLKATPIESHQVEKRKCNTATCATQRLANFLVHSSNNFGAILSSTNVGSNTYGKRNAVEVLKREPLNYLPL
Biochem/physiol Actions
IAPP (islet amyloid polypeptide) is secreted by the pancreatic β-cells along with insulin. IAPP is known to be involved in the regulation of gastric emptying, satiety and inhibiting glucagon secretion. IAPP is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus where IAPP is part of amyloid deposits and is associated with mass and functional loss of β-cells. Oligomers and fibrils formed by IAPP is known to be toxic to the pancreatic islet β-cells.
Physical form
Solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
N G Copeland et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 262(5130), 57-66 (1993-10-01)
Technological advances have made possible the development of high-resolution genetic linkage maps for the mouse. These maps in turn offer exciting prospects for understanding mammalian genome evolution through comparative mapping, for developing mouse models of human disease, and for identifying
Michele F M Sciacca et al.
Biophysical journal, 111(1), 140-151 (2016-07-15)
Our knowledge of the molecular events underlying type 2 diabetes mellitus-a protein conformational disease characterized by the aggregation of islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) in pancreatic β cells-is limited. However, amyloid-mediated membrane damage is known to play a key role in
Influence of Aluminium and EGCG on Fibrillation and Aggregation of Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide.
Xu ZX
Journal of Diabetes Research, 2016:1867059, 1-14 (2016)
The Role of Cholesterol in Driving IAPP- Interactions.
Sciacca MF
Biophysical Journal, 111(1), 140-151 (2016)
Zhi-Xue Xu et al.
Journal of diabetes research, 2016, 1867059-1867059 (2017-01-12)
The abnormal fibrillation of human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP) has been implicated in the development of type II diabetes. Aluminum is known to trigger the structural transformation of many amyloid proteins and induce the formation of toxic aggregate species. The
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service