SRP2015
RNA Polymerase II, p14.5 subunit human
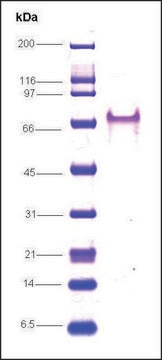
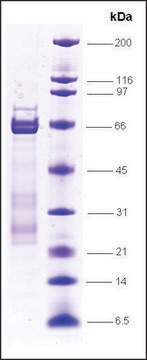
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonym(s):
RPB9, hRPB14.5
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
form
frozen liquid
mol wt
~16.6 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentration
300 μg/mL
technique(s)
western blot: suitable
color
clear colorless
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... POLR2I(5438)
Biochem/physiol Actions
hRPB9 is a subunit unique to RNA polymerase II, although it has sequence homologues in RNA polymerases I and III. The gene for Rpb9 is not essential for yeast cell viability, but is essential in Drosophila. hRPB9 has roles in both transcription initiation and transcription elongation. In the initiation reaction it is necessary for accurate start site selection. In the elongation reaction, RPB9, along with TFIIS facilitates the conversion of an arrest-competent conformation to a read-through competent conformation. RNA polymerase II lacking the RPB9 subunit uses alternate transcription initiation sites in vitro and in vivo and is unable to respond to the transcription elongation factor TFIIS in vitro. A role in the modulation of initiation and elongation is consistent with the localization of RPB9 in the three-dimensional structure of yeast RNA polymerase II. RPB9 is located at the tip of the so-called "jaws" of the enzyme, which is thought to function by clamping the DNA downstream of the active site. RPB9 comprises two zinc ribbon domains joined by a conserved linker region. The C-terminal zinc ribbon is similar in sequence to that found in TFIIS.
Physical form
Clear and colorless frozen liquid solution
Preparation Note
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. While working, please keep sample on ice.
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Harrison, D.A., et al.
Molecular and Cellular Biology, 11, 928-935 (1992)
Y Nogi et al.
Molecular and cellular biology, 13(1), 114-122 (1993-01-01)
We have previously isolated mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that are primarily defective in transcription of 35S rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I and have identified genes (RRN1 to RRN9) involved in this process. We have now cloned the RRN4 gene
N A Woychik et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 266(28), 19053-19055 (1991-10-05)
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II subunit gene RPB9 was isolated and sequenced. RPB9 is a single copy gene on chromosome VII. The RPB9 sequence predicts a protein of 122 amino acids with a molecular mass of 14,200 Da. The
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service