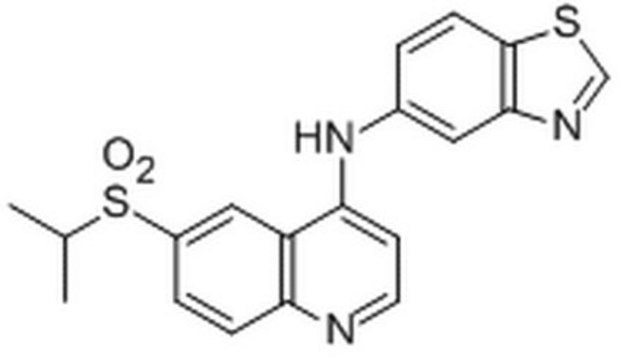
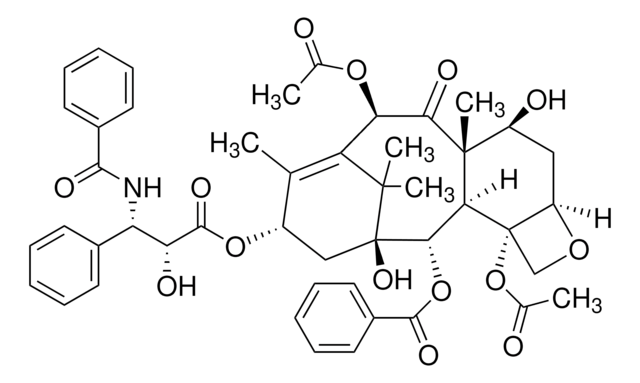
SRP2090
RAD51 human
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
Synonym(s):
BRCC5, HRAD51, HsRad51, HsT16930, RAD51A, RECA
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
≥80% (SDS-PAGE)
form
frozen liquid
mol wt
~39.1 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentration
500 μg/mL
technique(s)
electrophoretic mobility shift assay: suitable
color
clear colorless
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... RAD51(5888)
General description
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Preparation Note
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service