General description
We are committed to bringing you greener alternative products, which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Green Chemistry.This antibody is Preservative-free, produced without the harm or sacrifice of animals and exceptionally stable to allow for ambient shipping and storage if needed and thus aligns with "Waste Prevention", "Designing Safer Chemicals" and "Design for Energy Efficiency".
Click here for more information.
ZooMAb® antibodies represent an entirely new generation of recombinant monoclonal antibodies.Each ZooMAb® antibody is manufactured using our proprietary recombinant expression system, purified to homogeneity, and precisely dispensed to produce robust and highly reproducible lot-to-lot consistency. Only top-performing clones are released for use by researchers. Each antibody is validated for high specificity and affinity across multiple applications, including its most commonly used application. ZooMAb® antibodies are reliably available and ready to ship when you need them.
Specificity
Clone 1N16 is a ZooMAb® Rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody that specifically detects Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIP1). It targets an epitope within 22 amino acids from the N-terminal half.
Immunogen
KLH-conjugated linear peptide corresponding to 22 amino acids from the N-terminal half of human Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIP1).
Application
Quality Control Testing
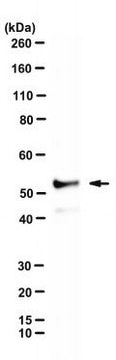
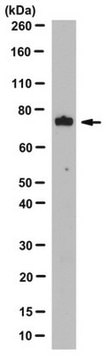
Evaluated by Western Blotting in NIH3T3 cell lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution of this antibody detected RIP1/RIPK1 in NIH3T3 cell lysate.
Tested applications
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution from a representative lot detected RIP1/RIPK1 in MCF7, A549, and Raw264.7 cell lysates.
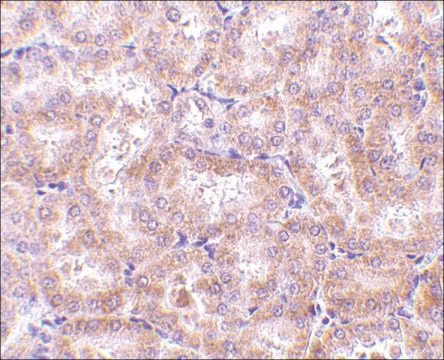
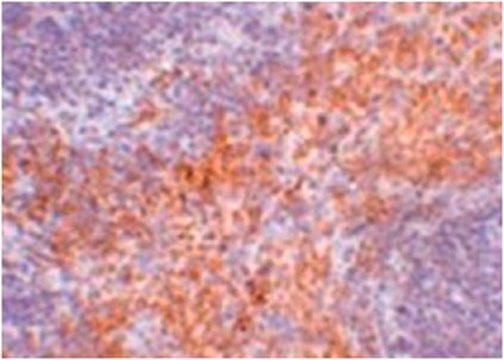
Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution from a representative lot detected RIP1/RIPK1 in human small intestine tissue sections.
Affinity Binding Assay: A representative lot of this antibody bound RIP/RIPK1 peptide with a KD of 2.3 x 10-7 in an affinity binding assay.
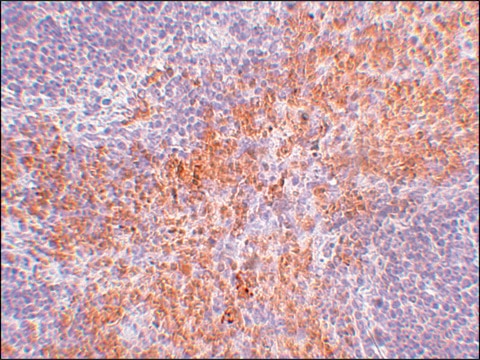
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A 1:100 dilution from a representative lot detected RIP1/RIPK1 in HT-29 cells.
Note: Actual optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user as specimens, and experimental conditions may vary with the end user
Target description
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (UniProt: Q13546; also known as EC:2.7.11.1, Cell death protein RIP, Receptor-interacting protein 1, RIP-1, RIPK1) is encoded by the RIPK1 (also known as RIP, RIP1) gene (Gene ID: 8737) in human. RIPK1 is a serine-threonine kinase that serves as a key regulator of TNF-a-mediated apoptosis, necroptosis, and inflammatory pathways. It exhibits kinase activity-dependent functions that regulates cell death and kinase-independent scaffold functions that regulate inflammatory signal transduction and cell survival. Upon binding of TNF-a to TNFR1, RIPK1 is recruited to the TNF-R1 signal transduction complex where it acts as a scaffold protein promoting cell survival, in part, by activating the canonical NF-kB pathway. RIPK1 is required to limit caspase 8-dependent TNFR1-induced apoptosis. Under normal conditions, RIPK1 acts as an inhibitor of RIPK3-dependent necroptosis via FADD-mediated recruitment of caspase 8, which cleaves RIPK1 (at Asp 324) and limits TNF-a-induced necroptosis. It is also required to inhibit apoptosis and necroptosis during embryonic development where it acts by preventing the interaction of TRADD with FADD thereby limiting aberrant activation of caspase 8. In addition to apoptosis and necroptosis, it is also involved in inflammatory response by promoting transcriptional production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. RIPK1 and RIPK3 are known to undergo reciprocal auto- and trans-phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of RIPK1 at Ser 161 by RIPK3 is crucial for the formation of the necroptosis-inducing complex. Its phosphorylation at Ser 25 represses its kinase activity and consequently prevents TNF-a-mediated RIPK1-dependent cell death. This ZooMAbZooMAb® recombinant monoclonal antibody, generated by our propriety technology, offers significantly enhanced specificity, affinity, reproducibility, and stability over conventional monoclonals. (Ref.: Dondelinger, Y., et al. (2019). Nat. Commun. 10(1); 1729; Meng, H., et al. (2018). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 115(9); E2001-E2009; He, S., et al. (2009). Cell. 137(6); 1100-1111).
Physical form
Purified recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody IgG, lyophilized in PBS, 5% Trehalose, normal appearance a coarse or translucent resin. The PBS/trehalose components in the ZooMAb formulation can have the appearance of a semi-solid (bead like gel) after lyophilization. This is a normal phenomenon. Please follow the recommended reconstitution procedure in the data sheet to dissolve the semi-solid, bead-like, gel-appearing material. The resulting antibody solution is completely stable and functional as proven by full functional testing. Contains no biocide or preservatives, such as azide, or any animal by-products. Larger pack sizes provided as multiples of 25 μL.
Reconstitution
300 μg/mL after reconstitution at 25 μL per vial. Please refer to guidance on suggested starting dilutions and/or titers per application and sample type.
Storage and Stability
Recommend storage of lyophilized product at 2-8°C; Before reconstitution, micro-centrifuge vials briefly to spin down material to bottom of the vial; Reconstitute each vial by adding 25 μL of filtered lab grade water or PBS; Reconstituted antibodies can be stored at 2-8°C, or -20°C for long term storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaws.
Legal Information
ZooMAb is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.