724823
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), amine terminated
average Mn 2,500 (T)
Synonym(s):
NIPAM polymer, PNIPAM-NH2, Polyacrylamide, functionalized polyNIPAM, functionalized polyacrylamide, polyNIPAM
About This Item
Recommended Products
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), or PNIPAM, is a stimuli-responsive polymer that responds to changes in pH and temperature and has a LCST around 32 C.
Tissue engineering has become a key therapeutic tool in the treatment of damaged or diseased organs and tissues, such as blood vessels and urinary bladders.
By altering the physicochemical properties, smart or intelligent drug delivery systems can be designed to deliver therapeutic molecules on-demand. Learn more about the application of stimuli-responsive materials in drug delivery.
Wide range of functional polymers for biomedical applications have been synthesized and structurally characterized. Several classes of polymers including biodegradable polymers, hydrophilic & amphiphilic polymers, and stimuli responsive polymers have been prepared using controlled and directed functionalization via "living" polymerization such as RAFT, ionic and ring opening polymerization. Selected polymers have been studied for their structure-properties relationship. "
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service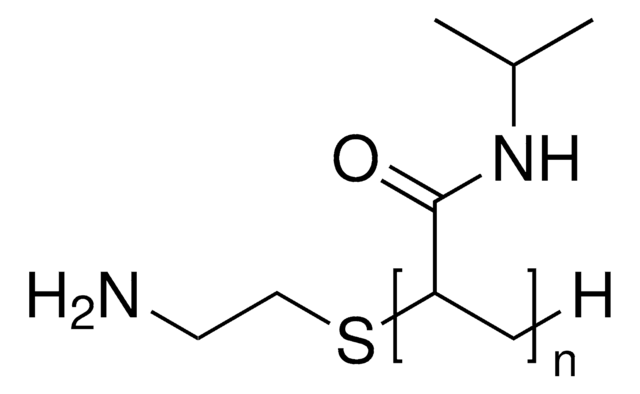
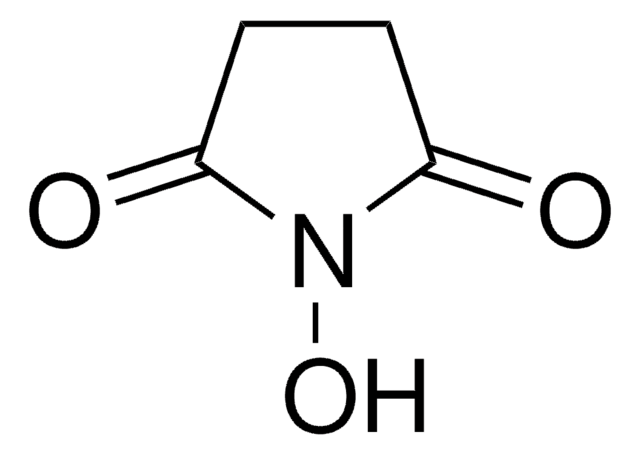
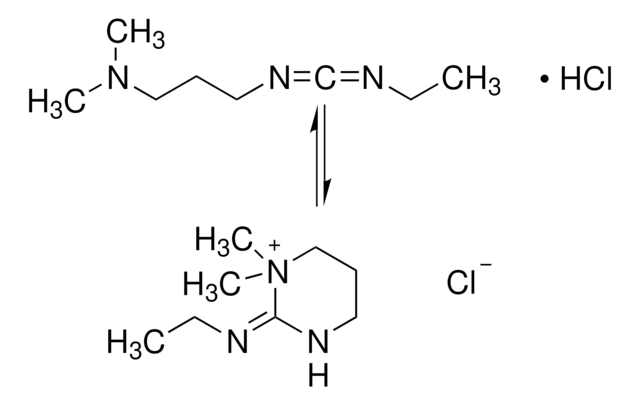
![O-[(N-Succinimidyl)succinyl-aminoethyl]-O′-methylpolyethylene glycol average Mn 750](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/244/886/c80fd8d8-9a62-4a97-be17-32d83ffd1dfb/640/c80fd8d8-9a62-4a97-be17-32d83ffd1dfb.png)