05-1338
Anti-Dimethyl Histone H3 (Lys4) Antibody, clone CMA303
clone CMA303, from mouse
Synonym(s):
H3K4me2, Histone H3 (di methyl K4), H3 histone family, member T, histone 3, H3, histone cluster 3, H3
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
CMA303, monoclonal
species reactivity
human, vertebrates
technique(s)
ChIP: suitable
ELISA: suitable
dot blot: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
multiplexing: suitable
western blot: suitable
isotype
IgG1κ
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
target post-translational modification
dimethylation (Lys4)
Gene Information
human ... H3C1(8350)
Related Categories
General description
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Sonicated chromatin prepared from HeLa cells (1 X 106 cell equivalents per IP) were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation using 2 µg of either a normal mouse IgG, or Anti-dimethyl-Histone H3 (Lys4) antibody and the Magna ChIP G (Cat. # 17-611) Kit. Successful immunoprecipitation of dimethyl-histone H3 (Lys4) associated DNA fragments was verified by qPCR using ChIP Primers GAPDH Coding.
Please refer to the EZ-Magna G ChIP (Cat. # 17-409) or EZ-ChIP (Cat. # 17-371) protocol for experimental details.
Dot Blot Analysis:
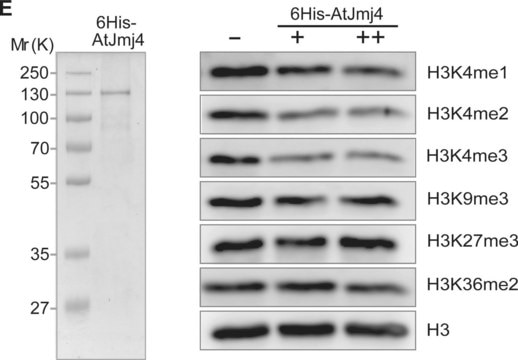
Absurance Histone H3 Antibody Specificity Array (Cat. No. 16-667) and Absurance Histone H2A, H2B, H4 Antibody Specificity Array (Cat. No. 16-665), which contain histone peptides with various modifications were probed with Cat. No 05-1338, Anti-dimethyl H3 (Lys4), clone CMA303 at 2.0 µg/mL (1:500 dilution). Proteins were visualized using a Donkey anti-mouse IgG conjugated to HRP and a chemiluminescence detection system.
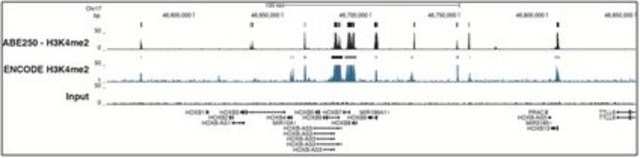
ChIP-seq Analysis:
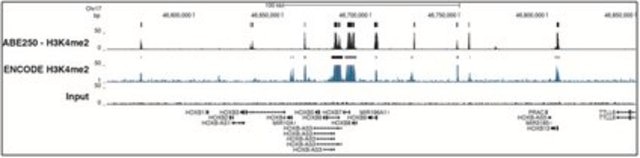
Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed using the Magna ChIP HiSens kit (cat# 17-10460), 2 µg of Anti-dimethyl-Histone H3 (Lys4) antibody (cat# 05-1338), 20 µL Protein A/G beads, and 1e6 crosslinked HeLa cell chromatin followed by DNA purification using magnetic beads. Libraries were prepared from Input and ChIP DNA samples using standard protocols with Illumina barcoded adapters, and analyzed on Illumina HiSeq instrument. An excess of sixteen million reads from FastQ files were mapped using Bowtie (http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/manual.shtml) following TagDust (http://genome.gsc.riken.jp/osc/english/dataresource/) tag removal. Peaks were identified using MACS (http://luelab.dfci.harvard.edu/MACS/), with peaks and reads visualized as a custom track in UCSC Genome Browser (http://genome.ucsc.edu) from BigWig and BED files. The highest 25% of peaks identified in the 04-790 and 05-1338 datasets showed 92 and 90% overlap with peaks identified in the ENCODE H3K4me2 BROAD Histone track for HeLa S3.
Immunocytochemistry:
This antibody has been shown by an outside laboratory to be suitable for immunocytochemistry.
Immunoprecipitation:
This antibody has been shown by an outside laboratory to be suitable for immunoprecipitation.
ELISA:
This antibody has been shown by an outside laboratory to be suitable for ELISA
Multiplexing:
This antibody specifically recognizes histone H3 dimethylated on Lys4 by Luminex assay.
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Histones
Quality
Western Blot Analysis: 2 μg/mL (1:500) dilution of this antibody detected dimethyl Histone H3 (Lys4) on 10 μg of HeLa acid extract.
Target description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
Analysis Note
HeLa Acid extract lysate
Other Notes
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service