11388908910
Roche
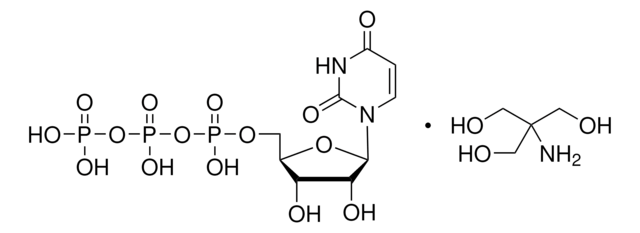
Biotin-16-UTP
pkg of 25 μL (250 nmol; 10mM)
Synonym(s):
Biotin-16-UTP, biotin
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41116100
Recommended Products
assay
97.7% (HPLC)
Quality Level
form
solution
mol wt
Mr 987.5 (biotin-16-UTP-Li4)
packaging
pkg of 25 μL (250 nmol; 10mM)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
color
colorless
solubility
water: miscible
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
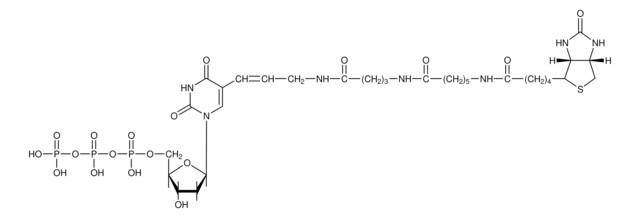
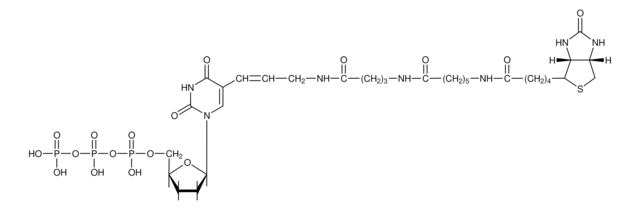
General description
For biotin-16-UTP, biotin is bound to uridine triphosphate via an amide linkage. Biotin-16-UTP is a substrate for SP6, T3, and T7 RNA polymerase. It can replace UTP in the in vitro transcription reaction for RNA labeling. Linearized template DNA with T7, SP6, or T3 promoter is in vitro-transcribed with the corresponding RNA polymerases using ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP, and Biotin-16-UTP, respectively.
Application
Biotin-labeled RNA can be used as a hybridization probe for:
- Northern blots
- Southern blots
- Plaque or colony lifts
- RNase protection experiments
- In situ hybridization
- Microarray hybridization
Quality
Typical analysis: At least 85% Biotin-16-UTP (HPLC, area%).
Physical form
Biotin-16-UTP, tetralithium salt, 10mM solution
Other Notes
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
does not flash
flash_point_c
does not flash
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Damian LaGamba et al.
Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists, 234(1), 132-142 (2005-07-13)
One of the most fundamental biological processes in development, as well as a primary mechanism for tumor metastasis, is epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT). To gain a greater understanding of this transition, we have obtained a genomic profile of the critical stages
Chenying Li et al.
Haematologica, 105(1), 148-160 (2019-04-13)
Homoharringtonine, a plant alkaloid, has been reported to suppress protein synthesis and has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Here we show that in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), homoharringtonine potently
Subramaniam Jayanthi et al.
PloS one, 4(6), e6092-e6092 (2009-07-01)
Methamphetamine (METH) is an illicit toxic psychostimulant which is widely abused. Its toxic effects depend on the release of excessive levels of dopamine (DA) that activates striatal DA receptors. Inhibition of DA-mediated neurotransmission by the DA D1 receptor antagonist, SCH23390
Aikaterini Tsaousi et al.
Circulation research, 108(4), 427-436 (2011-01-05)
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation causes intimal thickening in atherosclerosis and restenosis. Previously, we demonstrated that Wnt/β-catenin signaling upregulates VSMC proliferation in vitro. We examined this pathway in vivo and investigated the involvement of specific Wnt proteins in VSMC
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service