33801
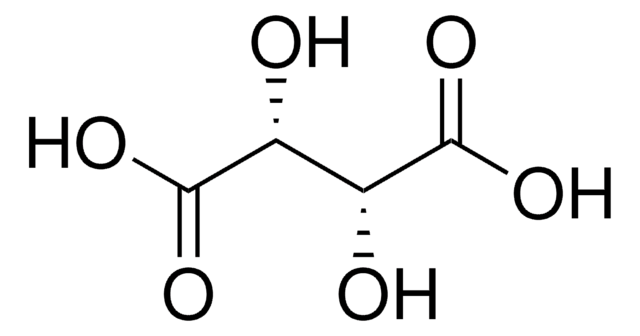
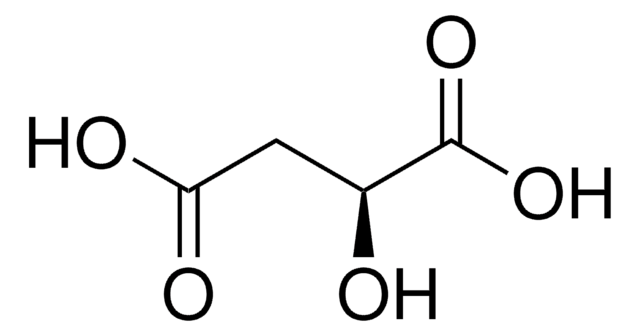
L-(+)-Tartaric acid
puriss. p.a., reag. ISO, 99.5-101.0% (calc. to the dried substance)
Synonym(s):
(2R,3R)-(+)-Tartaric acid, L-Threaric acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
agency
Ph. Eur.
USP/NF
reag. ISO
Quality Level
vapor density
5.18 (vs air)
grade
puriss. p.a.
assay
99.5-101.0% (calc. to the dried substance)
form
powder or crystals
optical activity
[α]20/D +12.0 to +12.8°, c = 20% in H2O
autoignition temp.
797 °F
impurities
≤0.0005% heavy metals (as Pb)
ign. residue
≤0.1% (as SO4)
loss
≤0.1% loss on drying, 105 °C
mp
170-172 °C (lit.)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤5 mg/kg
phosphate (PO43-): ≤10 mg/kg
sulfate (SO42-): ≤150 mg/kg
cation traces
Ca: ≤20 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤2 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
SMILES string
O[C@H]([C@@H](O)C(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O6/c5-1(3(7)8)2(6)4(9)10/h1-2,5-6H,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t1-,2-/m1/s1
InChI key
FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
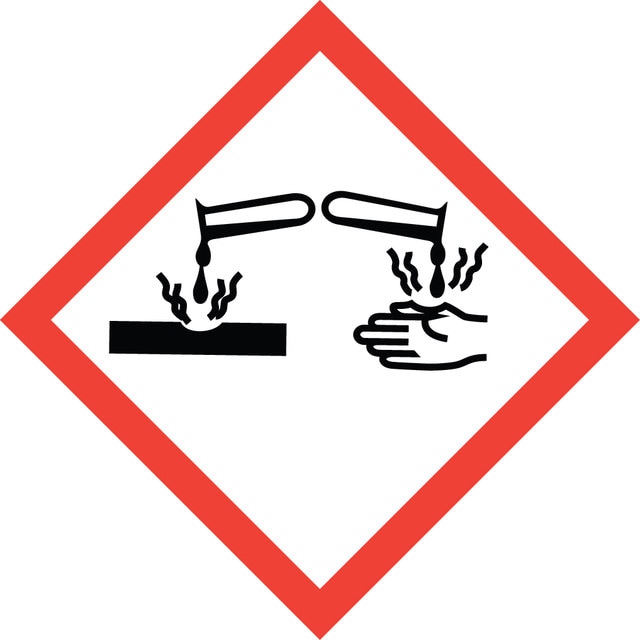
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
closed cup
flash_point_c
closed cup
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Protocols
Silica gel G 254 plates are suitable for analysis of Dextromethorphan following the European pharmacopeia monograph.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service