General description
IgG antibody subtype is the most abundant serum immunoglobulins of the immune system. It is secreted by B cells and is found in blood and extracellular fluids and provides protection from infections caused by bacteria, fungi and viruses. Maternal IgG is transferred to fetus through the placenta that is vital for immune defence of the neonate against infections. Anti-Mouse IgG (Fab specific)-FITC antibody is specific for Fab fragment of all mouse IgG subclasses. It shows no reactivity with mouse IgG, Fc fragment, or human IgG. Goat anti-Mouse IgG is conjugated to FITC and then purified by gel filtration to remove free FITC. The antibody is adsorbed with human IgG to ensure minimal cross reactivity.
Immunoglobulins (Igs) belong to the immunoglobulin super-family. The four classes of IgG include IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4.. The IgG heavy chain region is mapped to human chromosome 14. The immunoglobulin structure comprises of two heavy (H) and two light (L) chains, held together by disulfide linkages. The heavy chain has one variable N-terminal region and three to four constant (CH1-CH4) C-terminal regions. The L chain comprises of one variable N-terminal region and a constant C-terminal region.
Mouse IgG is a plasma B cell derived antibody isotype defined by its heavy chain. IgG is the most abundant antibody isotype found in mouse serum. IgG crosses the placental barrier, is a complement activator and binds to the Fc-receptors on phagocytic cells. The level of IgG may vary with the status of disease or infection.
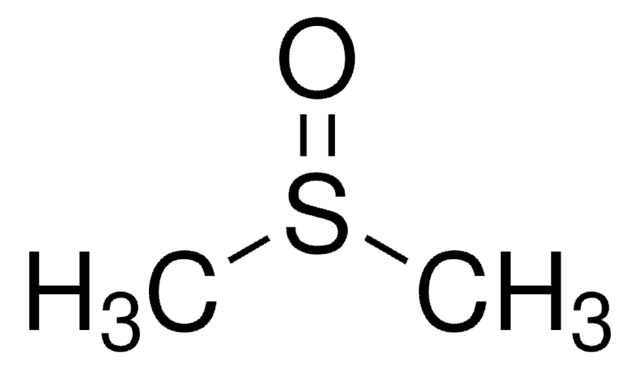
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a fluorescein derivative (fluorochrome) used to tag antibodies, including secondary antibodies, for use in fluorescence-based assays and procedures. FITC excites at 495 nm and emits at 521 nm.
Specificity
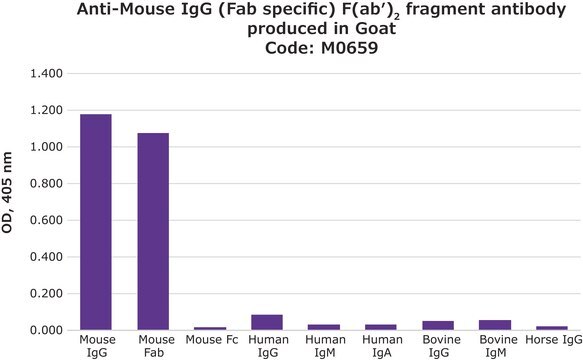
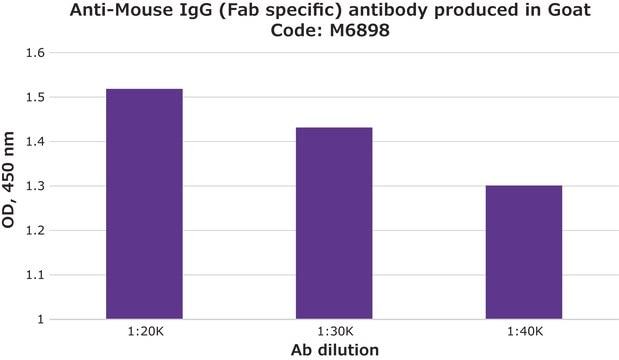
Specificity for the Fab fragment of mouse IgG is determined by immunoelectrophoresis (IEP). The conjugate shows no reactivity with mouse IgG, Fc fragment, or human IgG.
Immunogen
Purified mouse IgG, Fab fragment
Application
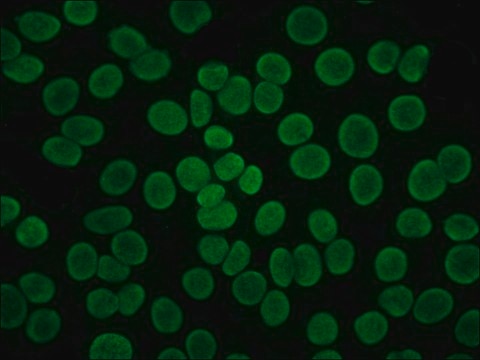
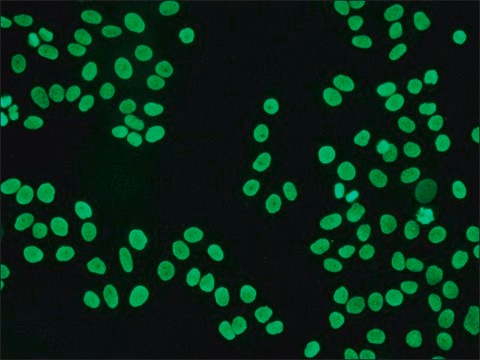
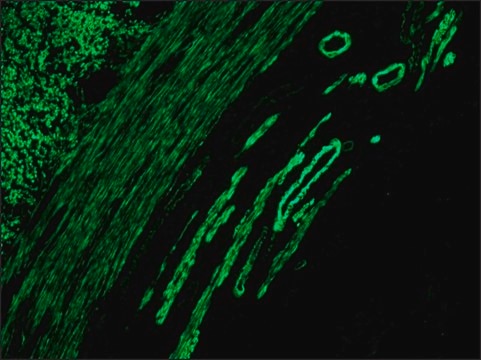
Anti-Mouse IgG (Fab specific) FITC antibody produced in goat has been used in:
- immunolocalization of pancreases or isolated islets
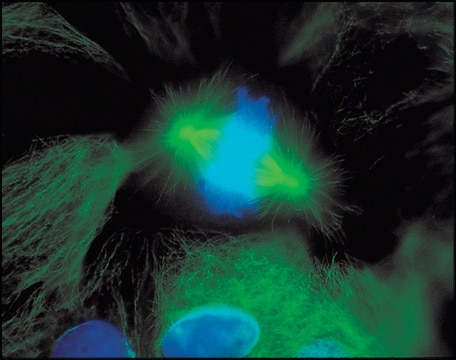
- immunocytochemistry analysis human tumor cell lines
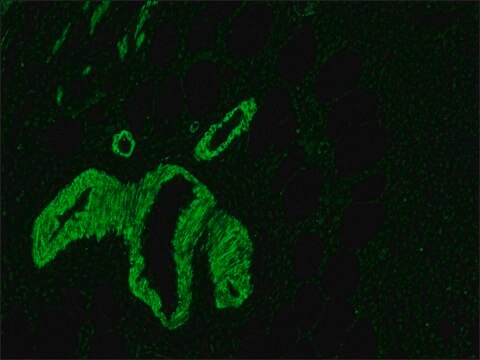
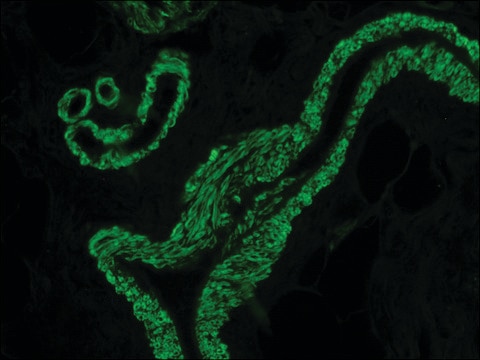
- immunohistochemistry of articular cartilage secondary antibody
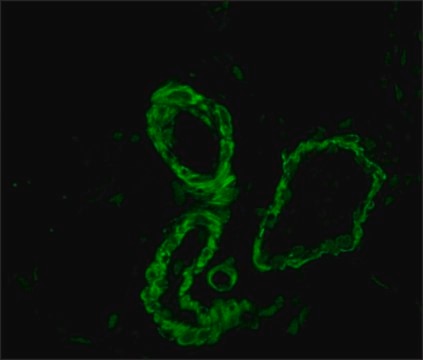
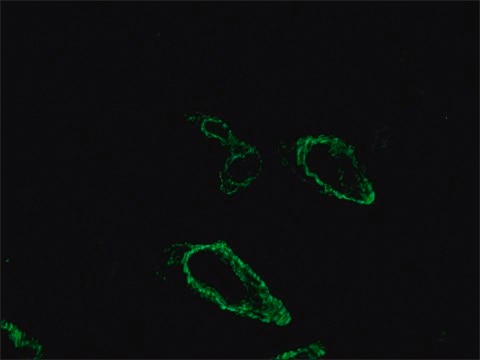
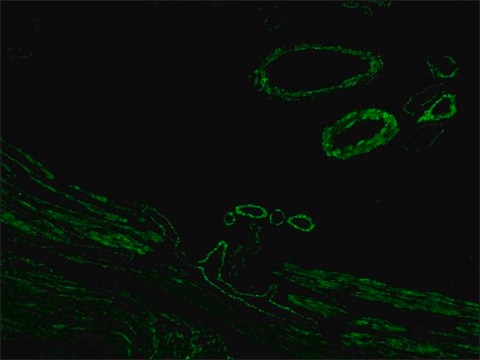
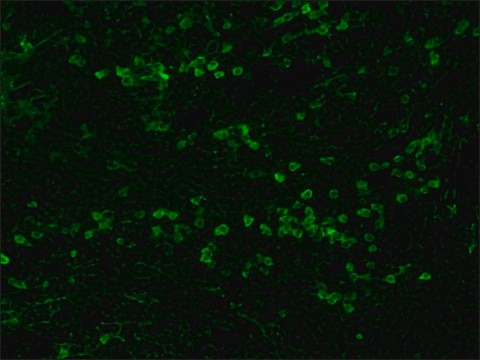
Anti-Mouse IgG (Fab specific)-FITC antibody may be used for immunofluorescence of human peripheral blood lymphocytes at a minimum dilution of 1:128. It may be used for imunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil slides at a working antibody dilution of 1:150. In an agar diffusion assay the conjugate produces a precipitation arc at a dilution of 1:32 versus a 1:80 dilution of normal mouse serum. The antibody was used at a dilution range of 1:50 to 1:300 for immunofluorescence in various studies.
Biochem/physiol Actions
IgG1 class is the most abundant and its deficiency results in hypogammaglobulinemia. IgG2 deficiency increases susceptibility to bacterial infections. IgG3 mediates effector functions. IgG4 is associated with asymptomatic infection. Digestion of IgG by papain results in generation of fragment antigen binding (Fab). Pepsin digestion of IgG results in fragment crystallizable (Fc). The Fc region of IgG antibody has enormous therapeutic potential and is exploited for the development of therapeutic antibodies.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Preparation Note
Adsorbed to reduce background staining with human samples.
Storage and Stability
For continuous use, store at 2-8 °C for a maximum of one month. For extended storage, the solution may be frozen in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in "frost-free" freezers, is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.