Recommended Products
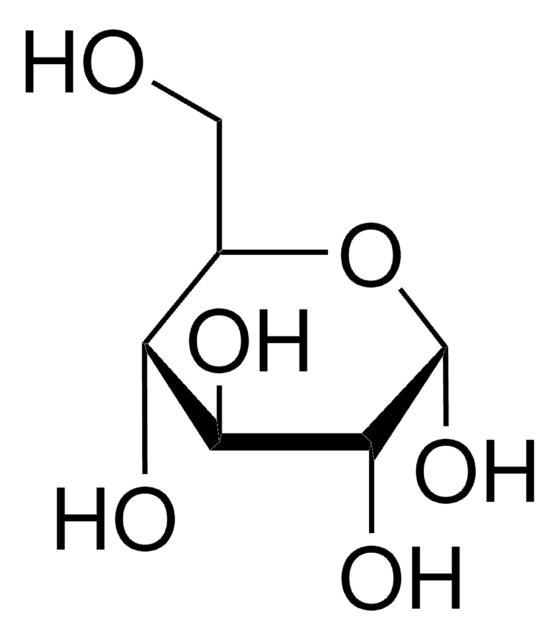
biological source
maize
Quality Level
description
Contains 0.1% (w/v) benzoic acid
form
liquid
concentration
1 mg/mL
application(s)
clinical testing
detection
format
single component solution
storage temp.
2-8°C
Related Categories
Application
The amount of glycogen in mouse muscle and liver tiβues was indirectly measured by analyzing the level of glycogen-derived glucose by an enzymatic-colorimetric glucose aβay kit using glucose standard solution to determine glycogen levels.
related product
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Jenny Fäldt et al.
Endocrinology, 145(6), 2680-2686 (2004-02-28)
IL-6 is produced and released in large amounts from skeletal muscle during prolonged exercise in both mice and humans, but there are few data indicating the biological significance of this. IL-6 exerts metabolic effects such as stimulating energy expenditure and
Jan Hubert et al.
Microbial ecology, 77(4), 1048-1066 (2018-11-23)
Interactions with microorganisms might enable house dust mites (HDMs) to derive nutrients from difficult-to-digest structural proteins and to flourish in human houses. We tested this hypothesis by investigating the effects of changes in the mite culture growth and population of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service