M9170
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor from mouse
M-CSF, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
mCSF-1, mM-CSF, CSF-1, M-CSF
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
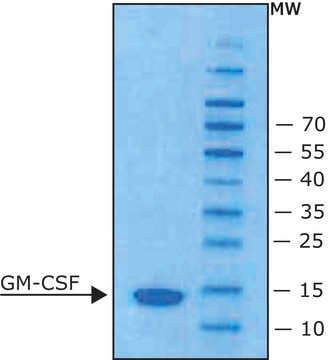
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
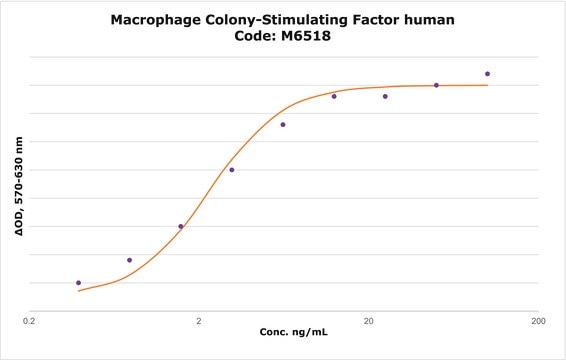
potency
0.500-3.000 ng/mL ED50
quality
endotoxin tested
mol wt
dimer 18.2 kDa (containing 156 amino acid residues)
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
≤1.000 EU/μg
color
white
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
mouse ... Csf1(12977)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- in the initiation of osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow monocyte cells
- to stimulate osteoclast differentiation in non-adherent hematopoietic cell
- for the generation of blood-derived stem cells
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Analysis Note
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service